Remembering the Legacy of Renowned Architect BV Doshi

B.V. Doshi is a renowned Indian architect who has made significant contributions to the field of architecture in India and around the world. He is known for his innovative designs and his commitment to sustainable and human-centered architecture.
Born in Pune, India in 1927, Doshi studied at the J.J. School of Architecture in Mumbai before traveling to the United States to study at the Illinois Institute of Technology under the guidance of the famous architect and urban planner, Ludwig Mies van der Rohe. Doshi’s time in the US had a profound influence on his architectural style and approach, and he brought many of the principles he learned there back to India with him.
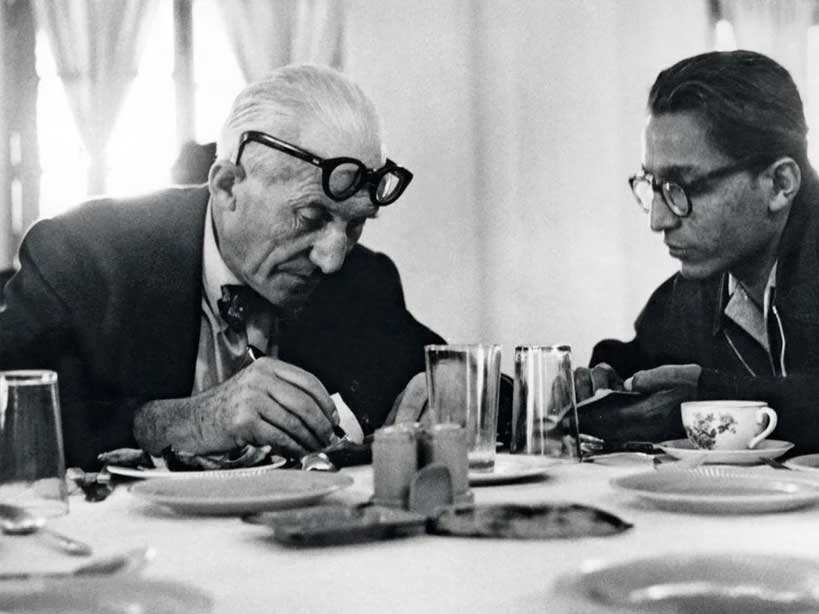

Upon his return to India, Doshi established his own architecture firm, Vastu-Shilpa (later known as Vastushilpa Consultants) and began working on a number of notable projects. One of his most famous works is the Indian Institute of Management in Ahmedabad, which is considered one of the most important architectural works of the 20th century in India. The building was designed in such a way as to be in harmony with its natural surroundings and to make use of passive cooling techniques to minimize the need for air conditioning.
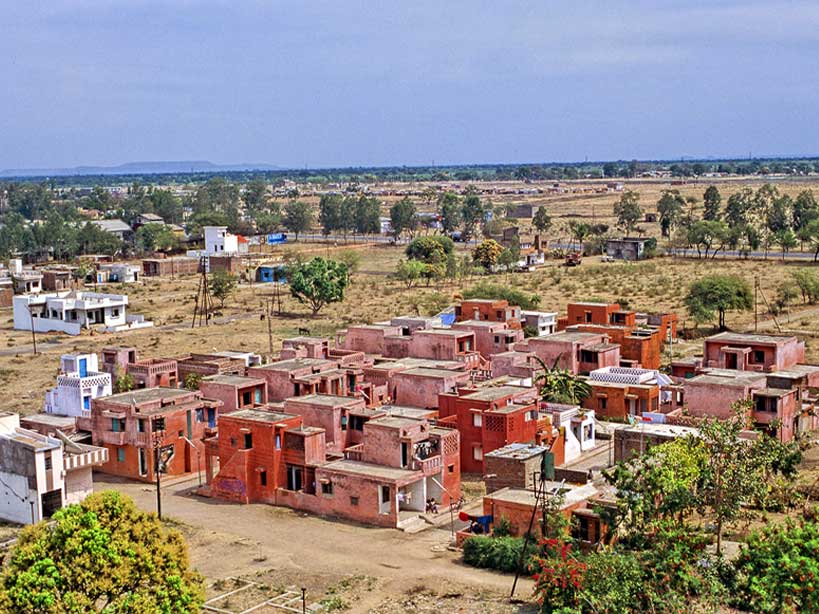

Doshi’s work is characterized by a deep understanding of the Indian context and culture, and he has been a vocal advocate for the use of traditional building techniques and materials in contemporary architecture. He has also been a strong supporter of the use of sustainable design principles in architecture, and has been a pioneer in the use of passive cooling techniques in buildings.
In 2018, Doshi was awarded the prestigious Pritzker Architecture Prize, which is often considered the highest honor in the field of architecture. In his acceptance speech, Doshi spoke of the importance of architecture in shaping our cities and our lives, and of the need for architects to think beyond the aesthetics of a building and to consider the broader social and environmental impact of their designs.

The philosophies of BV Doshi
Doshi’s philosophy is centered around the idea that architecture should be rooted in its context and culture, and that it should be responsive to the needs and aspirations of the people it serves. He has always believed that architecture should be “for the people, by the people, and of the people.” He has been an advocate for the use of traditional materials and techniques, and has incorporated many elements of traditional Indian architecture into his designs.
Doshi is also an advocate for the integration of the natural and built environments, and his designs often incorporate elements of nature, such as gardens, water features, and shading devices. He is also a strong proponent of sustainability, and his buildings are designed to minimize energy consumption and to be in harmony with the natural environment.
Top 10 notable works of Architect BV Doshi
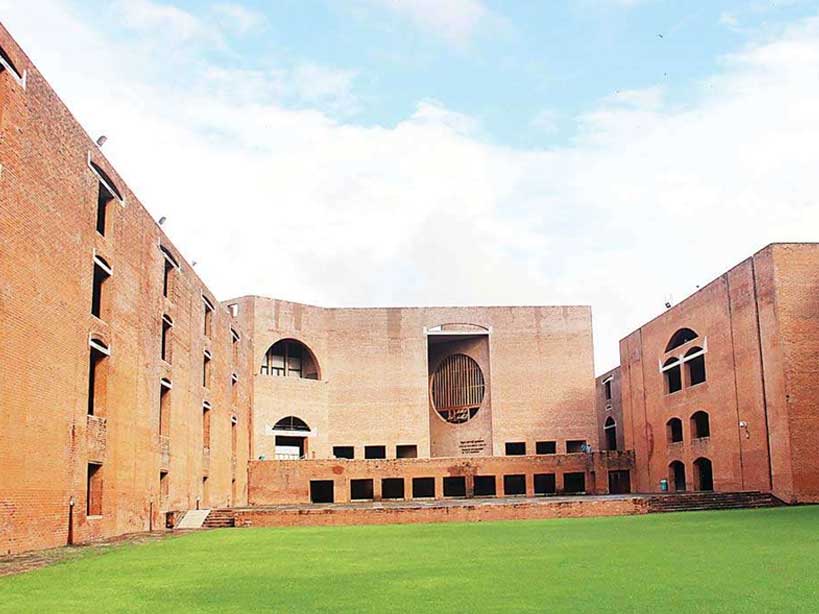
1. Indian Institute of Management (IIM) Ahmedabad
The building is designed to be in harmony with its natural surroundings, with the form and orientation of the building being carefully considered to make the most of the natural light and breezes. The use of passive cooling techniques, such as thick walls and shaded terraces, helps to keep the interior of the building cool, minimizing the need for air conditioning.
The building’s architecture is characterized by its use of traditional building techniques and materials, such as exposed brick and stone, which gives the building a unique character and connection to the local context and culture. The design of the building is also notable for its attention to detail and the use of clean lines and simple forms, which gives the building a timeless quality.

2. Aranya Low Cost Housing, Indore
This project was designed to provide affordable housing for low-income families and is notable for its use of low-cost materials and construction techniques, as well as its attention to the needs of the residents.
The housing development is also designed to be environmentally sustainable, with features such as solar water heaters and rainwater harvesting systems. The design of the development is also notable for its attention to detail and the use of clean lines and simple forms, which gives the development a timeless quality.

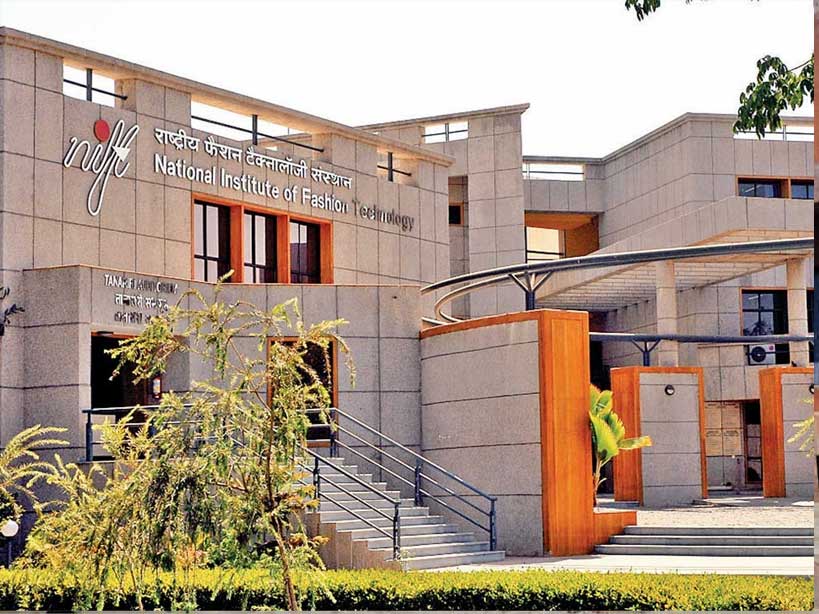
3. National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) Campus, Gandhinagar
The campus is known for its innovative design and use of sustainable principles. The NIFT Campus is designed to be environmentally sustainable, with features such as solar water heaters, rainwater harvesting systems, and the use of natural light and ventilation to minimize the need for artificial lighting and air conditioning. The campus also features a number of open spaces and gardens, which are designed to promote a sense of connection to nature and to provide a pleasant environment for students and staff.
The architecture of the campus is characterized by its use of traditional building techniques and materials, such as exposed brick and stone, which gives the campus a unique character and connection to the local context and culture. The design of the campus is also notable for its attention to detail and the use of clean lines and simple forms, which gives the campus a timeless quality.

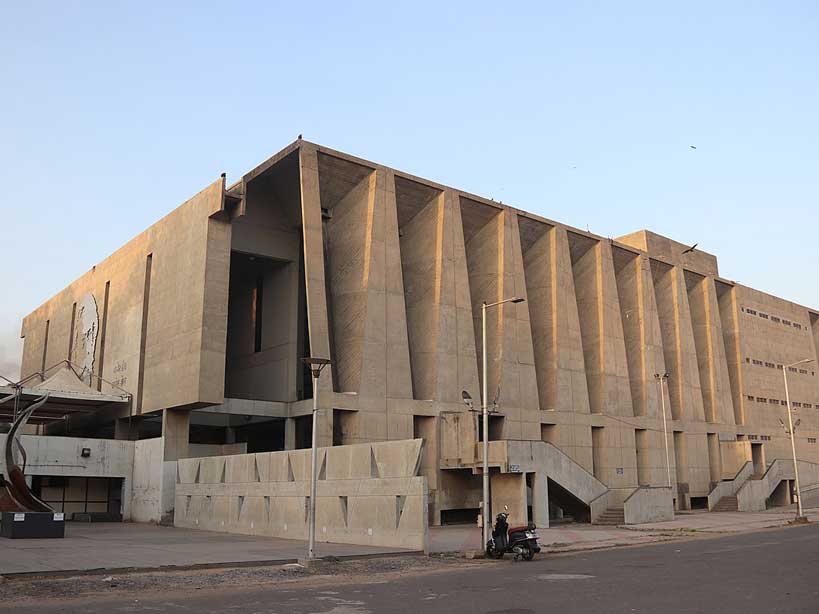
4.Tagore Memorial Hall, Ahmedabad
The hall’s architecture is characterized by its unique blend of traditional and modern architectural styles, which gives the hall a unique character and connection to the local context and culture. The design of the hall is also notable for its attention to detail and the use of clean lines and simple forms, which gives the hall a timeless quality.
The hall is designed to be a cultural center, with a number of different rooms and spaces that can be used for a variety of different activities. The hall also features a number of open spaces and gardens, which are designed to promote a sense of connection to nature and to provide a pleasant environment for visitors.
The hall is designed with a central courtyard, which is surrounded by the different spaces of the hall. This courtyard serves as the heart of the building, providing natural light and ventilation to the interior spaces, and also serves as a gathering space for the visitors.

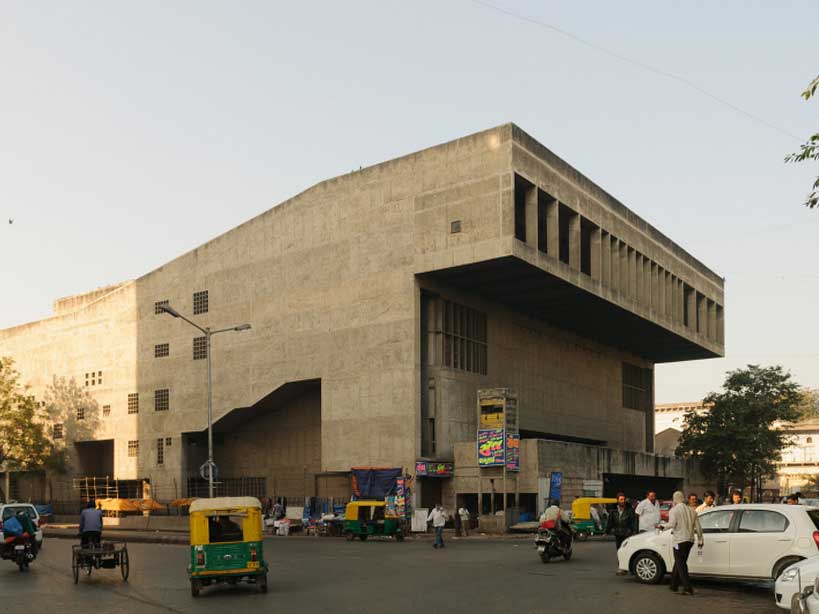
5.Premabhai Hall, Ahmedabad
Premabhai Hall is a cultural center and community space located in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India that was designed by renowned architect B.V. Doshi. The hall is known for its use of traditional building techniques and materials.
The hall’s architecture is characterized by its use of traditional building techniques and materials, such as exposed brick and stone, which gives the hall a unique character and connection to the local context and culture. The design of the hall is also notable for its attention to detail and the use of clean lines and simple forms, which gives the hall a timeless quality.

6. Shodhan Villa, Ahmedabad
The villa is known for its use of passive cooling techniques and its integration with its natural surroundings.
The villa is designed to be in harmony with its natural surroundings, with the building’s form and orientation being carefully considered to make the most of the natural light and breezes. The use of passive cooling techniques, such as thick walls and shaded terraces, helps to keep the interior of the building cool, minimizing the need for air conditioning.
The villa’s architecture is characterized by its use of traditional building techniques and materials, such as exposed brick and stone, which gives the villa a unique character and connection to the local context and culture.

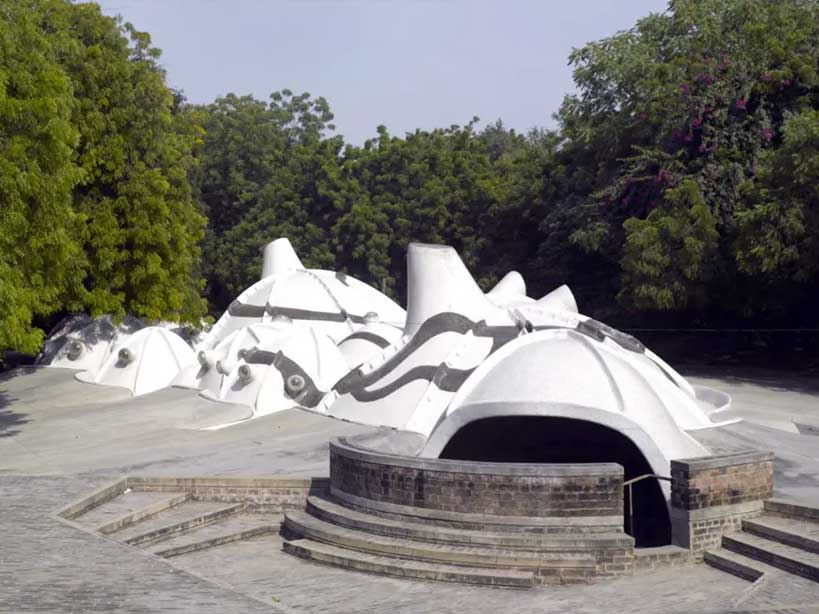
7. Amdavad ni Gufa, Ahmedabad
Amdavad ni Gufa is an underground art gallery located in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India that was designed by renowned architect B.V. Doshi. The gallery is known for its unique design and use of natural light.
The gallery is built underground, with a series of interconnected caves and caverns that are designed to provide a unique and immersive experience for visitors. The cave-like spaces are created using exposed concrete, which gives the gallery a raw and organic feel.
The use of natural light is a key feature of the design, with skylights and light wells used to bring natural light into the galleries and create a sense of connection to the outside world. The use of natural light also helps to minimize the need for artificial lighting, making the gallery more energy-efficient.

8. IIM Bangalore Campus
The campus is designed to be in harmony with its natural surroundings, featuring a number of environmentally sustainable design elements such as the use of passive cooling techniques to minimize the need for air conditioning, and the use of natural light and ventilation. The campus also features a number of open spaces and gardens, which are designed to promote a sense of connection to nature and to provide a pleasant environment for students and staff.
The architecture of the campus is characterized by its use of traditional building techniques and materials, such as exposed brick and stone, which gives the campus a unique character and connection to the local context and culture. The design of the campus is also notable for its attention to detail and the use of clean lines and simple forms, which gives the campus a timeless quality.
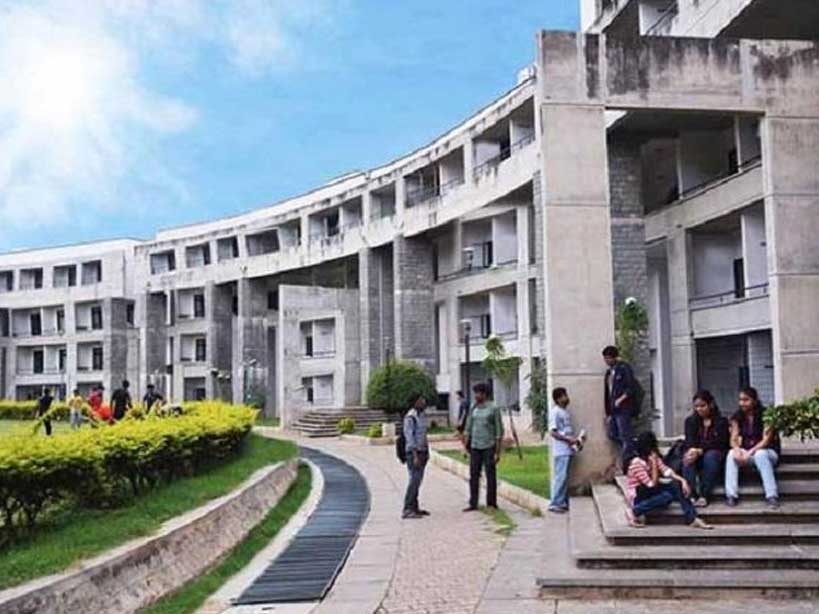

9.The Habitat Centre, New Delhi
The Habitat Centre is a complex located in New Delhi, India that was designed by renowned architect B.V. Doshi and his firm, Vastushilpa Consultants along with Architect Joseph Allen Stein. The complex is known for its innovative design and use of sustainable principles.
The Habitat Centre consists of a number of buildings, including an auditorium, a convention center, and a number of exhibition halls. The buildings are designed to be environmentally sustainable, with features such as solar water heaters, rainwater harvesting systems, and the use of natural light and ventilation to minimize the need for artificial lighting and air conditioning.
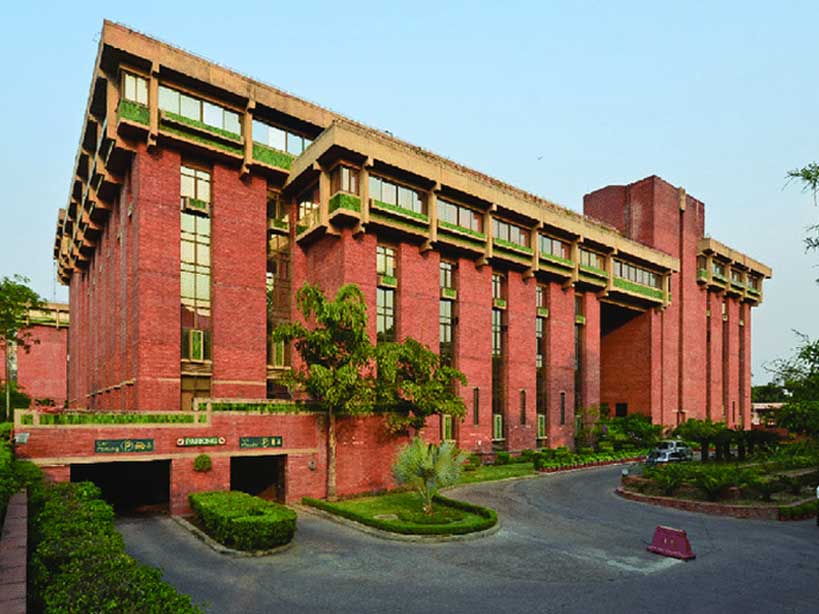

10. CEPT University, Ahmedabad
The CEPT University campus in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India is one of the most notable works of renowned architect B.V. Doshi. The campus was designed by Doshi and his firm, Vastushilpa Consultants, and was built over a period of several years starting in the early 1960s.
The CEPT University campus is known for its innovative design and use of sustainable principles. The campus is designed to be in harmony with its natural surroundings and features a number of environmentally sustainable design elements, such as passive cooling techniques to minimize the need for air conditioning, and the use of natural light and ventilation.

Photo Archival of BV Doshi
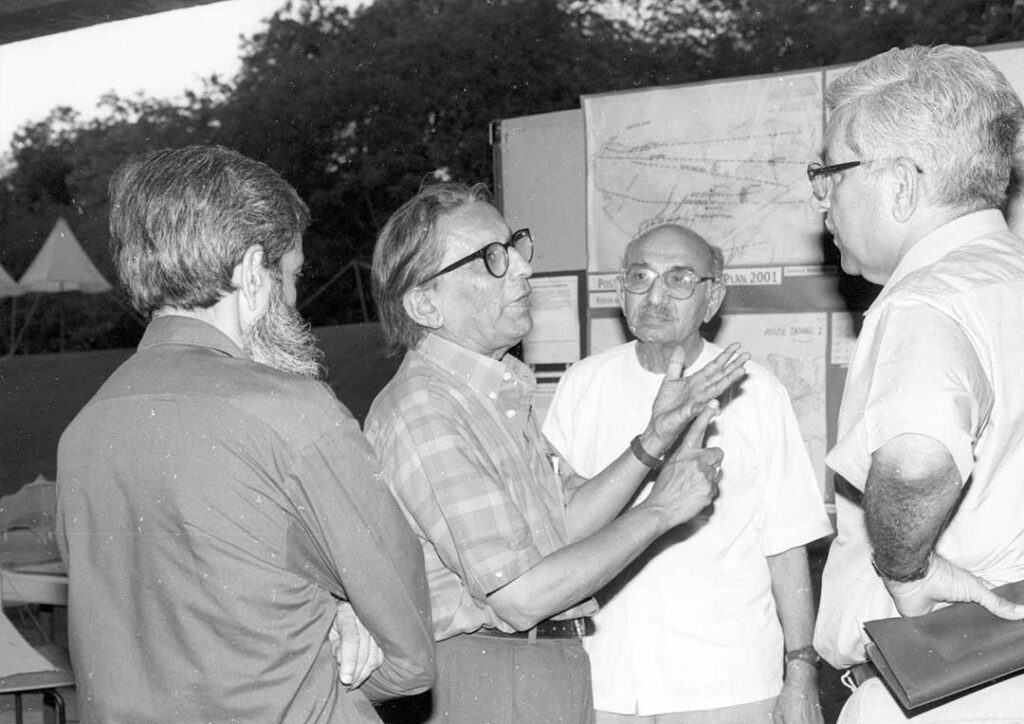
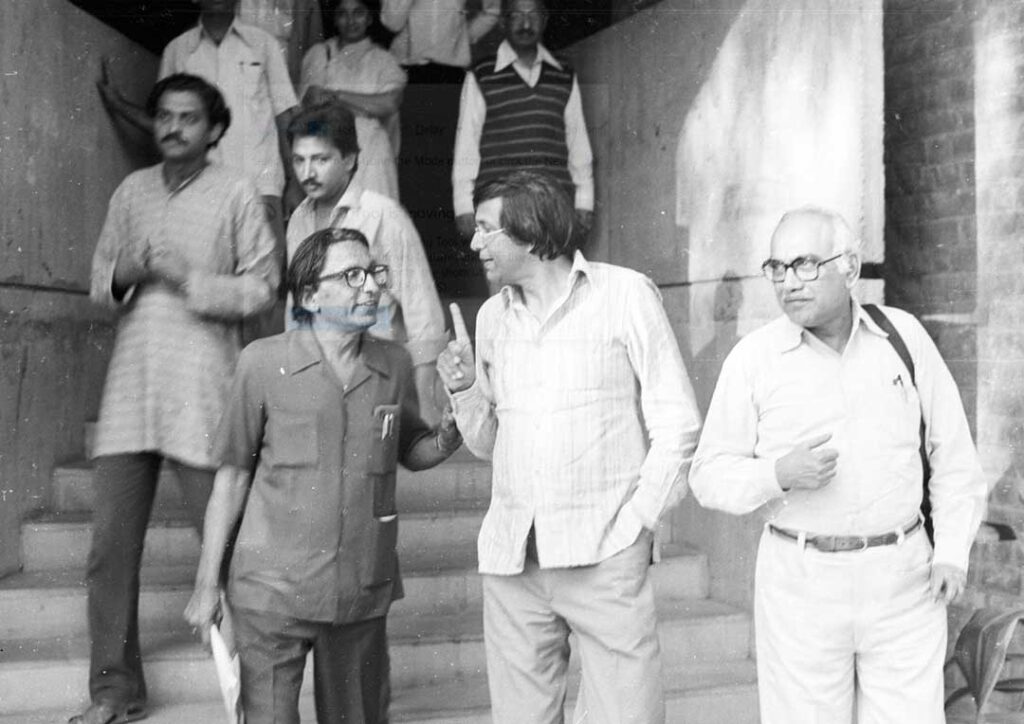









Remembering Balkrishna Doshi, (26 Aug 1927 – 24 Jan 2023)
Doshi’s legacy continues to be felt in the field of architecture today, and his work continues to inspire architects and designers around the world. Doshi’s passing is a great loss for the architecture community in India and around the world. His works and teachings will continue to inspire architects and urban planners for generations to come. His innovative designs, his commitment to sustainable and human-centered architecture and his deep understanding of the Indian context and culture, have made him one of the most important architects the century and his legacy will continue to inspire architects and designers for many years to come.

Urban Design Lab
About the Author
This is the admin account of Urban Design Lab. This account publishes articles written by team members, contributions from guest writers, and other occasional submissions. Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions or comments.
Related articles




Liu Jiakun wins 2025 Pritzker Architecture Prize


Best Architecture Design Quotes from the Legends
UDL GIS
Masterclass
GIS Made Easy – Learn to Map, Analyse, and Transform Urban Futures
Session Dates
23rd-27th February 2026

Urban Design Lab
Be the part of our Network
Stay updated on workshops, design tools, and calls for collaboration
Curating the best graduate thesis project globally!

Free E-Book
From thesis to Portfolio
A Guide to Convert Academic Work into a Professional Portfolio”
Recent Posts
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
Sign up for our Newsletter
“Let’s explore the new avenues of Urban environment together “