
Building Smarter Cities with GIS in Urban Planning
In today’s rapidly evolving urban landscapes, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are transforming the way cities are envisioned, planned, and managed. As a cornerstone of smart city development, GIS in urban planning integrates spatial data and advanced analytics to address urban challenges, foster sustainable growth, and enhance the quality of life for residents. This article delves into the pivotal role of GIS in crafting smarter, more resilient cities, highlighting key applications, successful case studies, and future trends shaping urban planning.
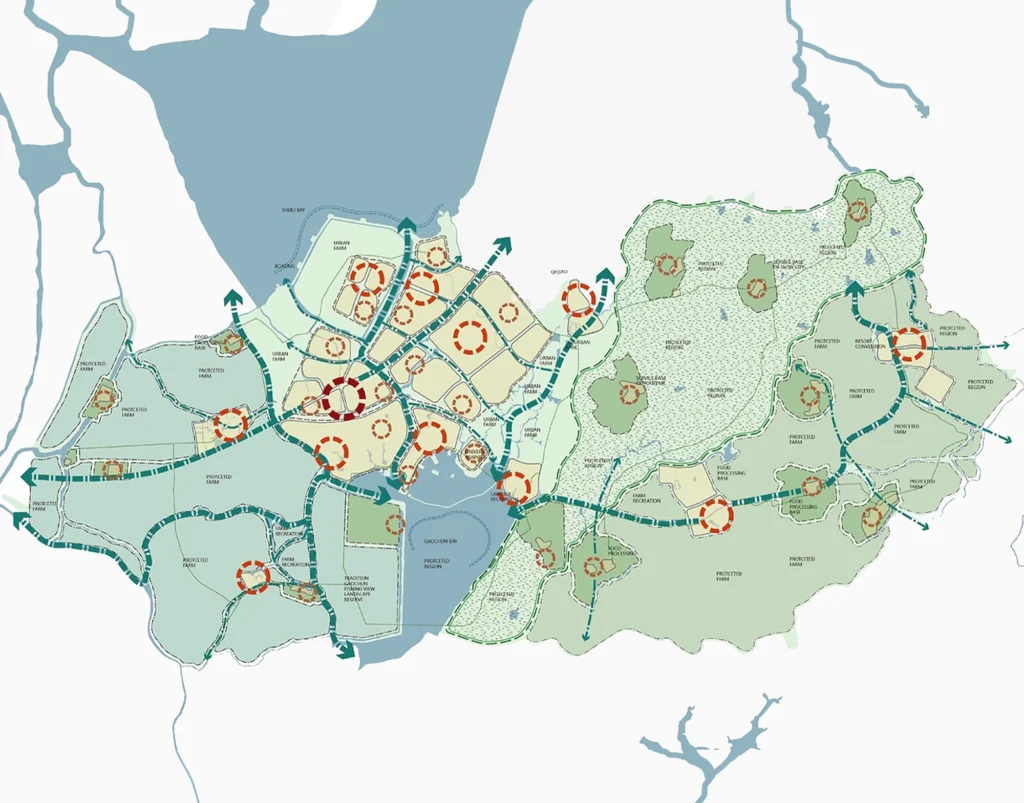
GIS As A Cornerstone Of Smart City Development: Core Applications
Urban Planning
- Land Use Planning: GIS facilitates the identification of optimal areas for various land uses, including residential, commercial, and industrial zones. By analyzing factors such as proximity to transportation networks, existing infrastructure, and natural resources, GIS ensures strategic and sustainable land allocation.
- Zoning: Implementing and enforcing zoning regulations is streamlined with GIS. The technology enables planners to delineate specific zones, ensuring that development adheres to established guidelines and maintains urban harmony.
- Urban Renewal: GIS plays a critical role in revitalizing underdeveloped or declining areas. By mapping and analyzing urban decay patterns, GIS assists in creating targeted redevelopment plans that rejuvenate communities and stimulate economic growth.
- Urban Growth Modeling: Predictive GIS models simulate future urban expansion under various scenarios. This foresight helps urban planners anticipate infrastructure needs, mitigate potential challenges, and guide sustainable city growth.
Transportation
- Traffic Management: GIS provides comprehensive visualization of traffic patterns, helping identify congestion hotspots and optimize traffic flow. Real-time data analysis enables dynamic traffic signal adjustments and better traffic management strategies.
- Public Transportation Planning: Efficient route planning for public transportation systems is achieved through GIS by considering population density, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. GIS ensures that public transit services meet the needs of the community while minimizing operational costs.
- Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS): Integration of GIS with ITS enhances the functionality of transportation networks. GIS supports the deployment of smart traffic lights, real-time monitoring systems, and adaptive traffic control measures that improve overall transportation efficiency.
Infrastructure
- Utility Network Mapping: GIS enables detailed visualization and management of underground utilities such as water, sewer, and electrical lines. This comprehensive mapping reduces maintenance costs, minimizes service disruptions, and enhances infrastructure reliability.
- Waste Management: Optimizing waste disposal facilities and collection routes is made possible with GIS. By analyzing waste flow data, GIS identifies the most efficient locations for waste management infrastructure and streamlines collection processes, promoting sustainability and cost savings.
- Emergency Response Planning: GIS is instrumental in creating effective emergency response strategies. It helps design evacuation routes, identify vulnerable areas, and simulate various emergency scenarios, thereby improving disaster preparedness and response capabilities.
GIS As A Cornerstone Of Smart City Development: Advanced Applications
Smart City Initiatives
- Smart Grids: GIS optimizes the distribution of electricity by identifying energy-efficient zones and managing renewable energy sources. This ensures a balanced and sustainable energy infrastructure, reducing costs and enhancing reliability.
- Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS): By analyzing traffic patterns, GIS helps optimize public transportation routes and implement ITS. This leads to improved urban mobility, reduced congestion, and a more efficient transportation network.
- Energy-Efficient Building Design: GIS assists in designing energy-efficient buildings, monitoring their performance, and managing facilities. This promotes sustainability, lowers operational costs, and enhances the overall energy management of urban environments.
Sustainability
- Environmental Impact Assessment: GIS evaluates the environmental impact of development projects, identifies sensitive areas, and develops effective mitigation strategies. This ensures that urban growth is sustainable and minimizes adverse environmental effects.
- Natural Resource Management: GIS manages essential natural resources such as water, forests, and wildlife habitats. By monitoring and optimizing the use of these resources, GIS supports the preservation and sustainable utilization of urban ecosystems.
- Climate Change Adaptation: GIS identifies climate change vulnerabilities, develops adaptation strategies, and assesses the effectiveness of mitigation measures. This contributes to building resilient urban infrastructure capable of withstanding environmental challenges.
Citizen Engagement
- Citizen Science Initiatives: GIS facilitates citizen science projects where residents collect and contribute data, enhancing urban planning and fostering community involvement. This collaborative approach empowers citizens and improves the accuracy of urban data.
- Community Mapping: GIS enables communities to create maps that reflect their unique needs and priorities. This fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment among residents, ensuring that urban development aligns with community values and requirements.
Data Analysis and Visualization
- Big Data Analytics: GIS analyzes large datasets from various sources, including sensors, social media, and mobile devices. This comprehensive analysis provides valuable insights for informed decision-making and strategic urban planning.
- Interactive Mapping: GIS creates interactive maps that allow users to explore data, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. These maps enhance transparency, engagement, and the overall understanding of urban dynamics.
- 3D City Models: GIS generates 3D models of cities to visualize development proposals, assess impacts, and improve public understanding. These models facilitate better planning, stakeholder communication, and visualization of future urban landscapes.
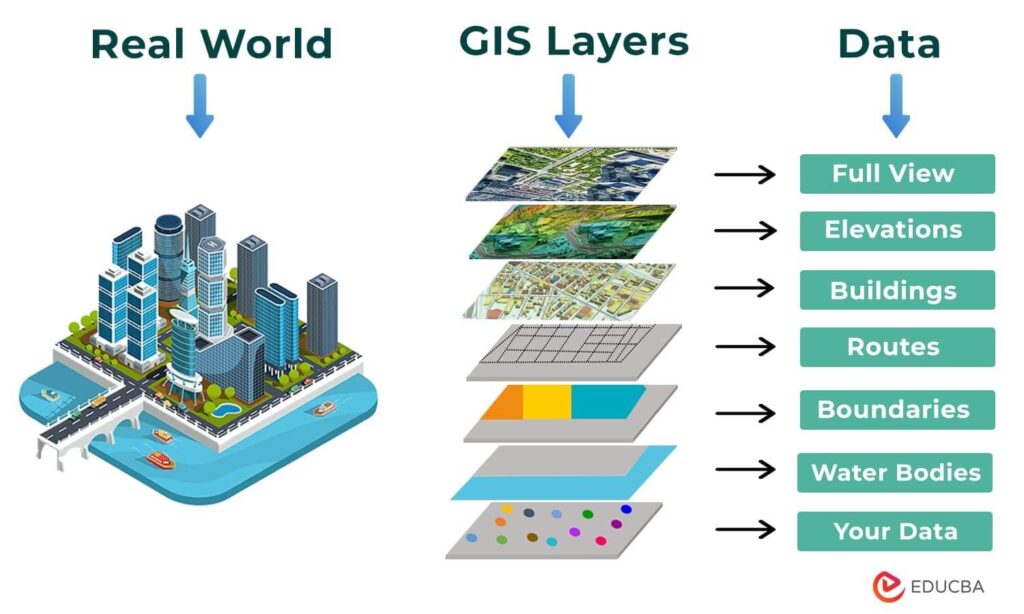
Source: Website Link
Most Popular GIS Software Tools
- ArcGIS by Esri leads the commercial GIS market, offering a comprehensive suite of tools for data management, spatial analysis, and advanced visualization, making it essential for urban planning and smart city development.
- QGIS is a powerful free and open-source GIS software renowned for its user-friendly interface and robust capabilities, providing urban designers with accessible solutions for geospatial analysis and mapping.
- Specialized GIS platforms like UrbanSim and TransCAD are pivotal for urban modeling and transportation planning, enabling planners to assess policy impacts, simulate urban growth, and optimize transportation networks effectively.
- 3D modeling software such as Rhino3D and Revit seamlessly integrate GIS functionalities, allowing architects and engineers to incorporate detailed spatial data into their designs, enhancing the precision and visualization of urban infrastructure projects.
- Open-source tools like GRASS GIS and GeoServer support advanced geospatial modeling and data sharing, fostering collaborative and sustainable urban planning initiatives by providing versatile platforms for managing and publishing spatial data.

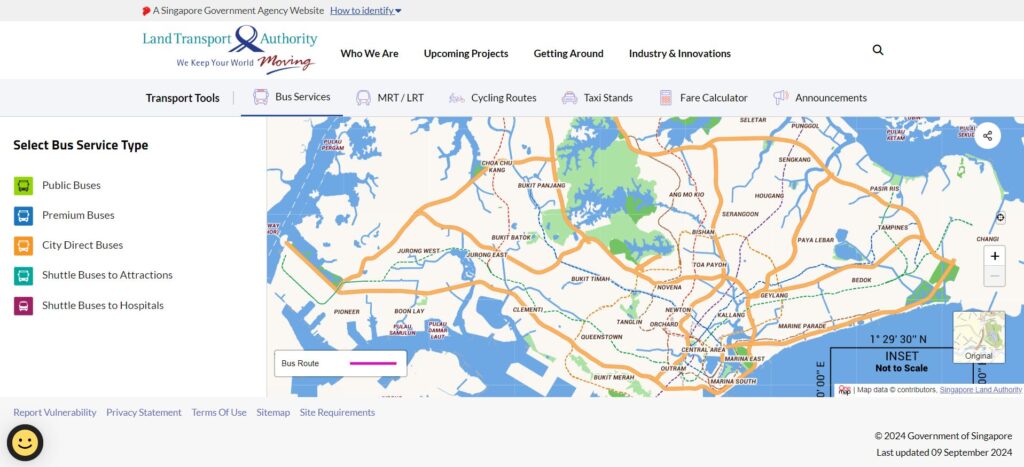
Successful Smart City Projects: Singapore
Singapore stands as a premier model for smart city development, leveraging Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to enhance various facets of urban planning and infrastructure. The Land Transport Authority (LTA) utilizes GIS to analyze traffic patterns, optimize signal timings, and implement intelligent traffic systems (ITS) such as real-time monitoring and electronic road pricing, significantly improving traffic flow and reducing congestion. In public transportation, GIS facilitates the planning and optimization of routes, ensuring efficient and reliable services, while the integration of contactless smart card payments streamlines the user experience. Singapore’s National Parks Board (NParks) employs GIS to manage green spaces, preserve biodiversity, and promote sustainable development by assessing ecological values, planning green corridors, and monitoring environmental conditions. Additionally, the National Environment Agency (NEA) uses GIS to optimize waste collection routes, track disposal facilities, and advance waste reduction and recycling initiatives. In the realm of smart infrastructure, the Energy Market Authority (EMA) harnesses GIS to develop smart grids, analyze power consumption patterns, identify grid vulnerabilities, and integrate renewable energy sources, thereby ensuring a more efficient and resilient electricity distribution network. Through these comprehensive GIS applications, Singapore effectively addresses urban challenges, fosters sustainable growth, and sets a benchmark for cities aspiring to become smarter and more resilient.
Successful Smart City Projects: Boston, Massachusetts
Boston and New York City exemplify successful community-based planning projects by leveraging Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to enhance citizen engagement and drive smart urban development. In Boston, the Planning & Development Agency (BP&D) has implemented interactive mapping tools that enable residents to explore zoning changes, review proposed development projects, and submit feedback, thereby increasing transparency and fostering public participation in the urban planning process. Additionally, Boston’s Neighborhood Planning initiatives utilize GIS to empower residents to identify community priorities, develop comprehensive neighborhood plans, and monitor progress, cultivating a strong sense of ownership and collaboration among citizens. Meanwhile, New York City’s Open Data Portal provides extensive datasets on crime, air quality, transportation, and demographics, promoting accountability and enabling city agencies and researchers to make informed policy decisions. The NYC Neighborhood Explorer, an interactive visualization tool, allows users to delve into neighborhood-level data on income, education, and health, facilitating targeted interventions and addressing specific community needs. These initiatives demonstrate how GIS applications in community-based planning can drive smarter, more inclusive urban development, setting a benchmark for other cities aiming to create resilient and responsive urban environments.
GIS Challenges and Solutions
GIS, while a powerful tool for urban planning, presents several challenges that must be addressed to maximize its effectiveness. Firstly, maintaining high data quality is essential, requiring rigorous validation and standardization processes to ensure accuracy and consistency. Secondly, integrating data from various sources can be complex; utilizing robust data integration frameworks and platforms can facilitate seamless data sharing across departments. Thirdly, safeguarding data privacy and security is critical, necessitating strong measures such as encryption and access controls to protect sensitive information. Additionally, the technical expertise required to operate GIS systems effectively highlights the need for comprehensive training and education programs to equip users with the necessary skills. Lastly, the cost of acquiring and maintaining GIS software and hardware can be prohibitive, making open-source alternatives and cloud-based solutions viable options to reduce expenses and enhance accessibility.

GIS and Emerging Technologies
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning enhance GIS by enabling predictive modeling and deep learning, allowing urban planners to analyze vast datasets to forecast trends like population growth and traffic congestion while identifying intricate patterns in geospatial data for land cover classification and object detection.
- Internet of Things (IoT) seamlessly integrates with GIS through sensor data, such as air quality monitors and traffic sensors, providing real-time insights into urban conditions that inform responsive and efficient city management.
- Blockchain Technology strengthens GIS by facilitating decentralized and secure data management, ensuring that geospatial information is shared efficiently and safely across various networks and organizations.
- Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality (AR/VR) revolutionize GIS applications by offering immersive experiences for visualizing and interacting with geospatial data, which enhances decision-making processes and stakeholder engagement in urban planning.
- Cloud Computing and 3D Printing provide scalable, on-demand access to powerful GIS tools and services while enabling the creation of tangible 3D models of urban environments, supporting effective planning, visualization, and communication of development proposals.

Future Trends: GIS and the Metaverse
- Digital Twins leverage GIS to create precise virtual replicas of cities, enabling detailed planning, simulation, and visualization within the metaverse for enhanced urban development strategies.
- Spatial Data Integration allows GIS to combine various data sources like building information models (BIM), sensor data, and historical maps, ensuring comprehensive and accurate metaverse environments that reflect real-world complexities.
- User Experience Enhancement utilizes GIS to deliver relevant spatial information and context within the metaverse, improving user interaction and understanding of virtual urban landscapes.
- Spatial Analysis with GIS facilitates essential tasks in the metaverse such as measuring distances, calculating areas, and identifying patterns, supporting applications in urban planning, resource management, and more.
- Virtual Tourism employs GIS to develop immersive virtual tours of real-world locations, providing users with the opportunity to explore destinations remotely, thereby promoting tourism and educational initiatives.

Future Trends: The Rise Of Custom GIS-Based Platforms
R.K Maps exemplifies the emerging trend of custom GIS-based platforms tailored to meet specific urban surveying needs. As a rapidly growing Egyptian enterprise, R.K Maps offers a versatile web and mobile application that streamlines data collection, analysis, and monitoring for urban planners and designers. Its key features include a user-friendly web-based interface, customizable survey forms that adapt to various project requirements, and a mobile app that facilitates real-time data collection and communication among surveyors. Additionally, R.K Maps provides flexible deployment options, supporting both on-premise and cloud-based solutions to accommodate diverse organizational needs. Unlike traditional commercial GIS software, R.K Maps stands out with its high level of affordability and customization, allowing clients to tailor the platform to their unique specifications. Enhanced security measures through on-premise deployment ensure that sensitive geospatial data is protected beyond the standards typically offered by commercial providers. Currently developing a demo for its official launch, R.K Maps is poised to introduce additional features and functionalities, further advancing the capabilities of custom GIS solutions in urban planning and smart city development.
Conclusion
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have emerged as indispensable tools for the development of smarter cities. By providing a framework for collecting, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data, GIS enables decision-makers to make informed choices and implement effective strategies. From urban planning and infrastructure management to environmental assessment and community engagement, GIS offers a wide range of applications that contribute to the creation of more sustainable, resilient, and equitable cities. As technology continues to advance, GIS will undoubtedly play an even more critical role in shaping the future of urban development.
References
- Adejoh, I. Y. (2015). APPLICATION OF GIS IN ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION NETWORK SYSTEM. European International Journal of Science and Technology.
- Creating a sustainable urban infrastructure with GIS data. (2023, August 22). Retrieved from fulcrum: https://www.fulcrumapp.com/blog/creating-a-sustainable-urban-infrastructure-with-gis-data
- Emergency Management. (n.d.). Retrieved from esri: https://www.esri.com/en-us/industries/emergency-management/overview
- Hanoon, S. K. (2023, February 20). Urban Growth Forecast Using Machine Learning Algorithms and GIS-Based Novel Techniques: A Case Study Focusing on Nasiriyah City, Southern Iraq. Retrieved from MDPI: https://www.mdpi.com/2220-9964/12/2/76
- Interactive Maps for Public Construction Projects. (n.d.). Retrieved from mapme: https://mapme.com/blog/interactive-maps-for-public-construction-projects/
- Public Transit. (n.d.). Retrieved from esri: https://www.esri.com/en-us/industries/transit/business-areas/route-planning-optimization
- Topuz, M., & Deniz , M. (2023, March 18). Application of GIS and AHP for land use suitability analysis: case of Demirci district (Turkey). Retrieved from Humanities and Social Sciences Communications: https://rdcu.be/dTGeN
- Unlocking GIS in Urban Planning: Benefits, Application & Examples. (2023, September 21). Retrieved from maptionnaire: https://www.maptionnaire.com/blog/gis-in-urban-planning-benefits-application-examples
- Unlocking the Power of GIS in Infrastructure Development: Mapping, Analysis, and Decision-Making. (2023, March 16). Retrieved from AKS: https://www.akhilesh.info/blogs/unlocking-the-power-of-gis-in-infrastructure-development-mapping-analysis-and-decision-making

Ahella Abdelghaffar
About the author
Born and raised in Egypt, Ahella pursued a degree in Urban Design at Cairo University. Her interests include Urban Design and mental health, as well as GIS applications in Urban Design.
Related articles


Remembering Frank O. Gehry: The Architect Who Redrew Skylines
Architecture Professional Degree Delisting: Explained
Periodic Table for Urban Design and Planning Elements


History of Urban Planning in India
UDL Illustrator
Masterclass
Visualising Urban and Architecture Diagrams
Session Dates
28th-29th March 2026

Urban Design Lab
Be the part of our Network
Stay updated on workshops, design tools, and calls for collaboration
Curating the best graduate thesis project globally!

Free E-Book
From thesis to Portfolio
A Guide to Convert Academic Work into a Professional Portfolio”
Recent Posts
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
Sign up for our Newsletter
“Let’s explore the new avenues of Urban environment together “






































2 Comments
An amazing article from a truly great person
Interesting article. This has exposed me to some critical information.