Big Data in Urban Design

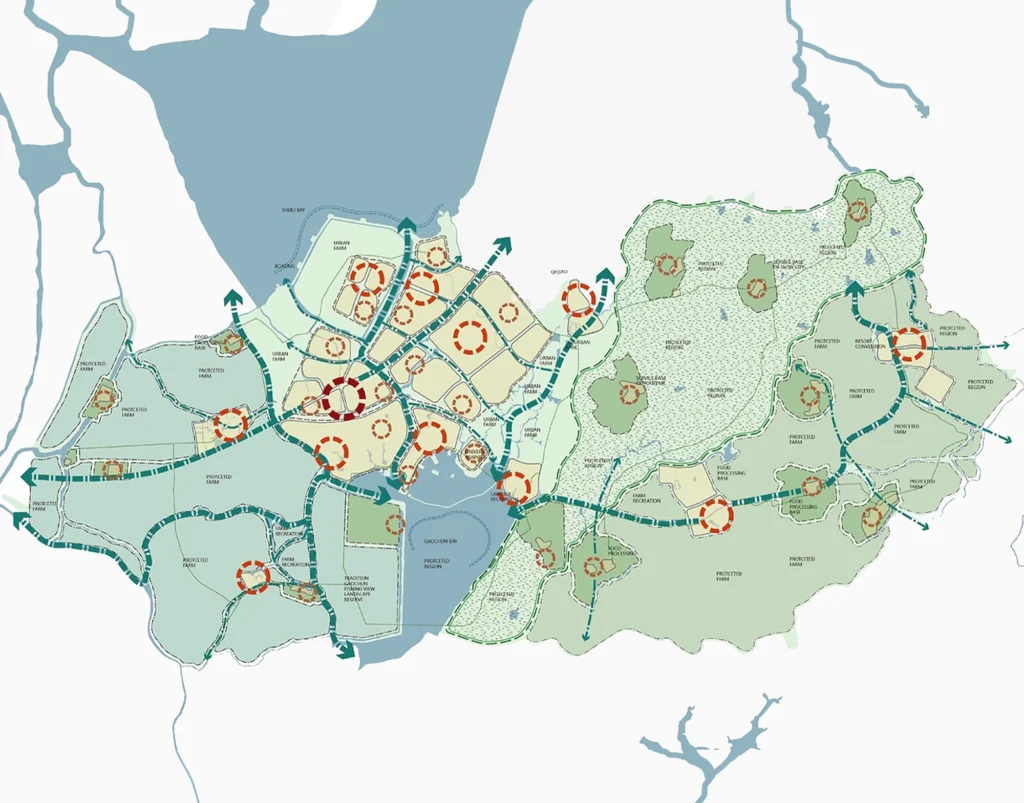
The rapid urbanization of cities has brought with it the need for more efficient and sustainable planning. Big data offers a transformative approach to urban design by allowing planners to make informed, data-driven decisions. This shift enables the creation of smarter cities that can adapt to the changing needs of their residents in real-time. The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), mobile devices, and social platforms provides urban planners with vast amounts of data, from traffic flow patterns to citizen feedback. Leveraging this information can lead to more sustainable infrastructure, improved services, and ultimately a better quality of life.
Data Sources for Urban Planning
Urban designers now have access to multiple data sources that can be used to improve city planning. GPS data from smartphones reveals how people move through a city, while sensors embedded in public infrastructure track traffic, weather, and environmental conditions. Social media offers real-time insights into public sentiment on urban issues. Each of these sources contributes to a broader understanding of how cities function. By combining data from different sources, planners can address issues like overcrowding, inefficient transport routes, and inadequate public amenities.
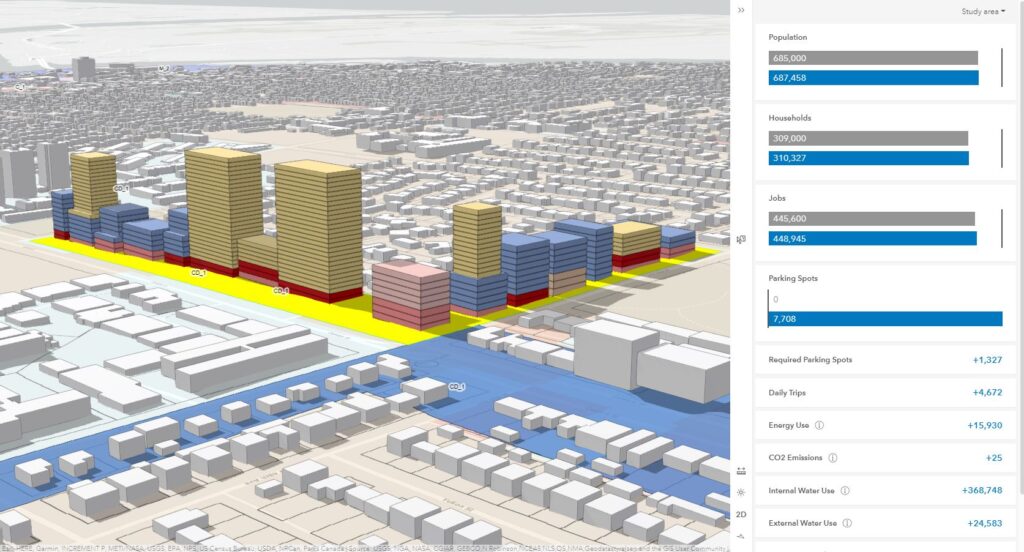
Enhancing Transportation Systems
Big data has revolutionized transportation systems in cities by allowing for dynamic, real-time solutions to congestion and inefficiencies. Data from traffic sensors, public transportation, and ride-sharing services provide insights into peak travel times and bottlenecks. This information enables cities to develop smart traffic systems that optimize signal timings and reduce congestion. Public transportation systems can adjust routes based on current demand, improving the overall efficiency of the network. With big data, planners can also predict future needs, ensuring that cities are prepared for population growth or unexpected events like natural disasters.
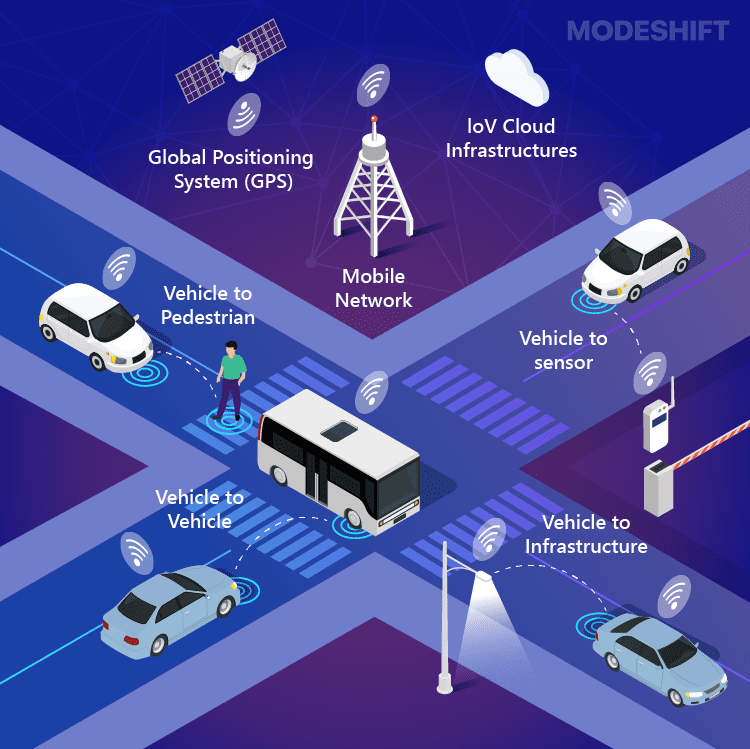
Source: Website Link
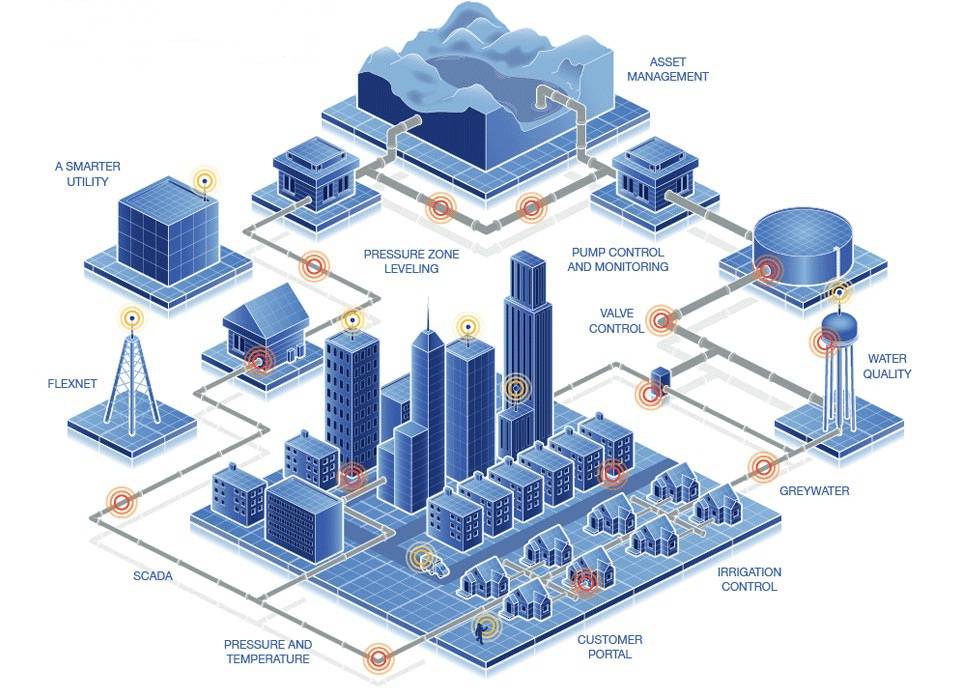
Smart Infrastructure and Resource Management
Big data is essential for designing smart infrastructure that maximizes resource efficiency. Urban infrastructure, from electricity grids to water systems, can be optimized through data analytics. Smart grids, for instance, adjust energy supply based on demand patterns, reducing waste and enhancing sustainability. In water systems, sensors detect leaks or inefficiencies, preventing water loss. These technologies not only contribute to more sustainable cities but also improve service reliability and reduce operating costs. As cities face increasing pressure from climate change and population growth, data-driven resource management is becoming a vital aspect of urban design
Public Safety and Crisis Management
In the realm of public safety, big data plays a pivotal role in enhancing crime prevention and crisis response. Predictive analytics can help law enforcement identify high-risk areas, allowing for more efficient allocation of resources. In times of crisis, such as natural disasters or health emergencies, real-time data from various sources, including social media and emergency services, helps cities respond more effectively. By analyzing patterns and real-time information, cities can deploy first responders faster, manage evacuations, and mitigate risks. This proactive approach leads to safer urban environments and better-prepared cities.
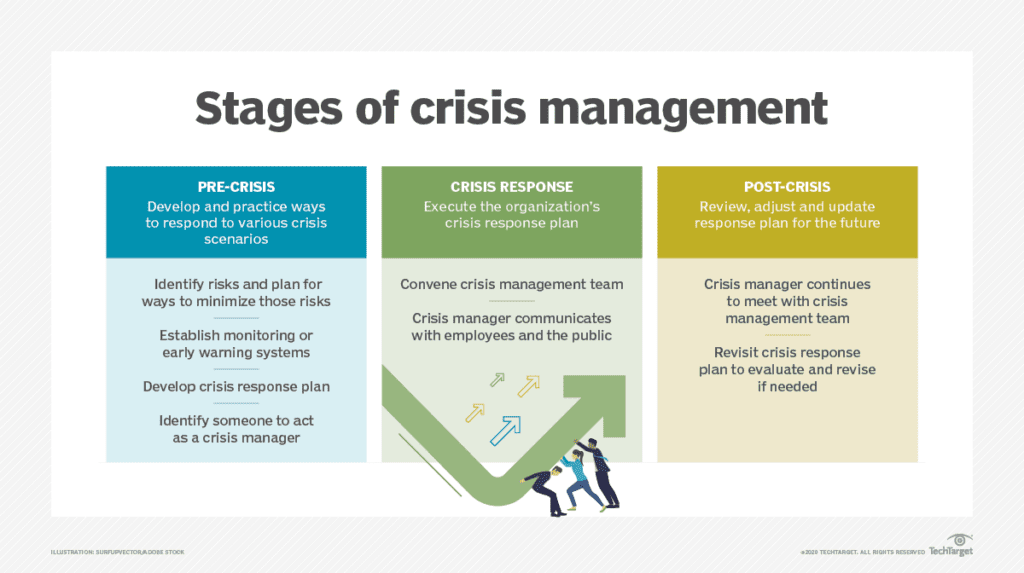
Engaging Citizens Through Data
Big data allows for greater citizen participation in urban design. Digital platforms enable residents to provide input on public projects, report infrastructure issues, or share opinions on city services. Smartphone apps, for instance, allow users to flag issues like potholes or damaged streetlights, making urban services more responsive. Social media platforms offer spaces for public feedback, creating a more transparent dialogue between citizens and planners. By including residents in the data collection and decision-making process, cities become more democratic and attuned to the needs of their communities.
Addressing Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Despite its many advantages, the use of big data in urban design raises significant ethical concerns. One of the primary issues is data privacy. With so much information being collected from citizens, ensuring data protection and preventing misuse is crucial. Another challenge is bias within the data itself. If the data used for decision-making is incomplete or skewed, it can lead to inequitable solutions that benefit certain groups at the expense of others. Cities must develop policies that safeguard privacy and ensure that big data is used in an ethical, fair manner.
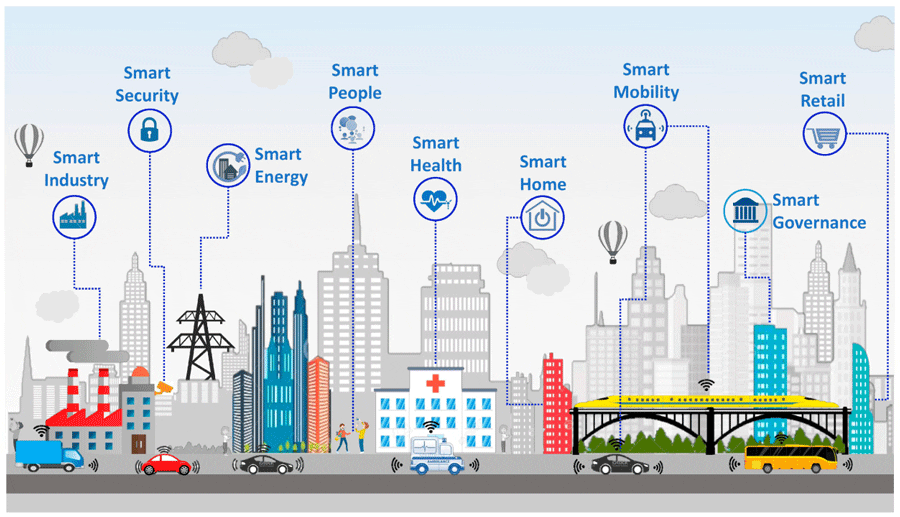
Building Technological Infrastructure for Smart Cities
For cities to fully benefit from big data, they must invest in the technological infrastructure that supports it. This includes deploying sensors, smart devices, and data processing platforms capable of analyzing vast amounts of information in real time. Additionally, cities need skilled data analysts and urban planners who can interpret the data and translate it into actionable insights. The development of urban data hubs where information from different sources can be aggregated is also essential. Without this infrastructure, cities risk lagging behind in the transition to becoming smarter and more efficient.
Future Directions in Data-Driven Urban Design
The future of urban design will increasingly depend on the integration of big data. As cities become more connected and the IoT expands, data-driven solutions will allow for even greater precision in urban planning. Innovations in AI and machine learning will further enhance the ability of cities to adapt and learn from the data they collect. From autonomous vehicles to personalized public services, data will play a central role in shaping urban experiences. However, the human element must remain at the core of these advancements to ensure cities are not only smart but also equitable and inclusive
-1
Conclusion
In conclusion, big data is revolutionizing urban design by providing city planners with the tools to make smarter, more informed decisions. By utilizing data from various sources, cities can optimize transportation, manage resources more efficiently, and improve public safety. Citizen engagement is also enhanced through data platforms, creating a more participatory urban design process. However, the widespread use of big data comes with challenges, including privacy concerns and the need for ethical frameworks. As technology continues to evolve, cities that embrace data-driven planning will be better equipped to meet the challenges of the future, creating urban environments that are not only smarter but also more sustainable, inclusive, and resilient.
References
Batty, M. (2018). “Artificial Intelligence and Urban Planning.” Urban Analytics and City Science, 45(5), 965-977.
- Silva, B. N., Khan, M., and Han, K. (2018). “Towards Sustainable Smart Cities: A Review of Trends, Architectures, Components, and Open Challenges in Smart Cities.” Sustainable Cities and Society, 38, 697-713.
- Batty, M. (2013). The New Science of Cities. MIT Press.
- Kitchin, R. (2014). The Data Revolution: Big Data, Open Data, Data Infrastructures & Their Consequences. SAGE Publications.
afnan Mohsin
About the Author
Afnan Mohsin is an author holding a Bachelor’s degree in Architecture and a Master’s degree in Urban Design from the University of Technology. With a profound interest in contemporary tools and sustainable design, she leverages her extensive academic background and professional expertise to advance innovative solutions in urban development. Her work emphasizes the integration of modern methodologies with sustainable practices, contributing to the creation of resilient and dynamic urban environments.
Related articles

Architecture Professional Degree Delisting: Explained
Periodic Table for Urban Design and Planning Elements


History of Urban Planning in India

Kim Dovey: Leading Theories on Informal Cities and Urban Assemblage
UDL GIS
Masterclass
GIS Made Easy – Learn to Map, Analyse, and Transform Urban Futures
Session Dates
23rd-27th February 2026

Urban Design Lab
Be the part of our Network
Stay updated on workshops, design tools, and calls for collaboration
Curating the best graduate thesis project globally!

Free E-Book
From thesis to Portfolio
A Guide to Convert Academic Work into a Professional Portfolio”
Recent Posts
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
Sign up for our Newsletter
“Let’s explore the new avenues of Urban environment together “