G20 Summit Insights for Urban Planning and Development

India's G20 Presidency: A Vision for a Sustainable Future
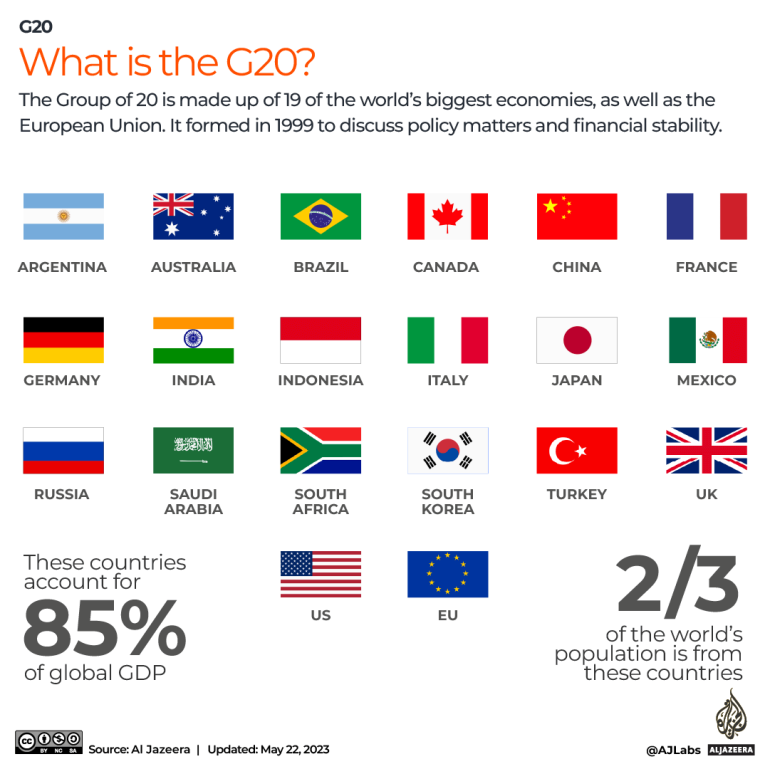
India has assumed the prestigious Presidency of the G20, a platform that brings together the world’s major economies, from December 1, 2022, to November 30, 2023. This period marks India’s opportunity to take the helm and steer the collective efforts of G20 nations toward addressing pressing global challenges. The pinnacle of India’s G20 Presidency is set to be the final New Delhi Summit in September the following year. What makes this occasion even more remarkable is the participation of a record-breaking 43 Heads of Delegations, making it the largest-ever gathering in the history of the G20 Summit.

A Vibrant Emblem
The visual identity of India’s G20 Presidency is encapsulated in its emblem, a design that evokes both the spirit of the nation and the collective aspirations of the G20 nations. Drawing inspiration from the colors of India’s national flag—saffron, white, green, and blue—the emblem is a harmonious blend of symbolism. It unites the image of our planet Earth with the lotus, India’s national flower. This symbolism represents growth, resilience, and the spirit of thriving amid adversity. The Earth in the emblem reflects India’s commitment to a pro-planet approach, one that is in perfect harmony with nature. Below the G20 logo, the word “Bharat” is written in the Devanagari script, a nod to India’s rich linguistic and cultural diversity.
"Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam" - One Earth · One Family · One Future
The theme chosen for India’s G20 Presidency is “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam,” a phrase derived from the ancient Sanskrit text of the Maha Upanishad. This theme, translated as “One Earth · One Family · One Future,” embodies the idea of universal kinship. It underscores the intrinsic value of all life forms—human, animal, plant, and even microorganisms—and highlights their interconnectedness on the planet Earth and in the broader cosmos. At its core, this theme champions the LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) movement, which promotes environmentally sustainable and responsible choices. These choices span individual lifestyles and national development trajectories, with the ultimate goal of catalyzing global transformation towards a cleaner, greener, and bluer future.

India's G20 Priorities

1. Green Development, Climate Finance & LiFE:
India’s first priority revolves around confronting climate change head-on. This includes not only addressing the complex issue of climate change but also paving the way for climate finance and technology to be accessible and effective for all nations. India recognizes that ensuring a just transition to clean energy is crucial, especially for developing countries. To this end, the country champions the LiFE movement, promoting environmentally conscious practices that align seamlessly with the overarching G20 theme of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” (One Earth · One Family · One Future).
2. Accelerated, Inclusive & Resilient Growth:
India understands that inclusive growth is not just an aspiration but a necessity for a sustainable global future. To achieve this, India’s G20 Presidency seeks to accelerate the integration of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) into the global trade ecosystem. By fostering the spirit of trade for growth, India aims to promote labor rights and welfare, bridging global skills gaps and creating a more equitable and inclusive world. Additionally, India focuses on building inclusive agricultural value chains and resilient food systems, acknowledging the vital role of agriculture in ensuring global food security.
3. Accelerating Progress on SDGs:
As the world reaches the midpoint of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, India’s G20 Presidency recognizes the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. It has transformed a decade of action into a decade of recovery. In this context, India reaffirms the commitment of the G20 to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). India’s focus is on navigating the global community through this crucial period, reinforcing the resolve to meet the SDGs, and taking concrete steps to address the challenges that have arisen in the wake of the pandemic.
4 Technological Transformation & Digital Public Infrastructure:
India champions a human-centric approach to technology within the G20. This approach emphasizes the need for technology to serve humanity’s well-being rather than merely be an end in itself. India encourages knowledge-sharing in critical areas such as digital public infrastructure, financial inclusion, and technology-driven development across sectors ranging from agriculture to education. By fostering the responsible and inclusive use of technology, India seeks to unlock its potential as a catalyst for global progress.
5. Multilateral Institutions for the 21st Century:
India’s G20 priority is to advocate for a reformed multilateral system—one that is more accountable, inclusive, just, equitable, and representative. In a rapidly changing world, India believes that the existing multilateral institutions must evolve to meet the challenges of the 21st century effectively. By pressing for these reforms, India aims to create a multipolar international system that can address the diverse and complex challenges of our times.
6. Women-Led Development:
India places a strong emphasis on women’s empowerment and representation as key drivers of inclusive growth and development. Recognizing the pivotal role women play in socio-economic development, India’s G20 Presidency strives to promote women to leadership positions and decision-making roles. By doing so, it seeks to foster an environment where women can contribute fully to the achievement of the SDGs, thereby advancing global development and gender equality.
G20 New Delhi Declaration - Endorsing Frameworks
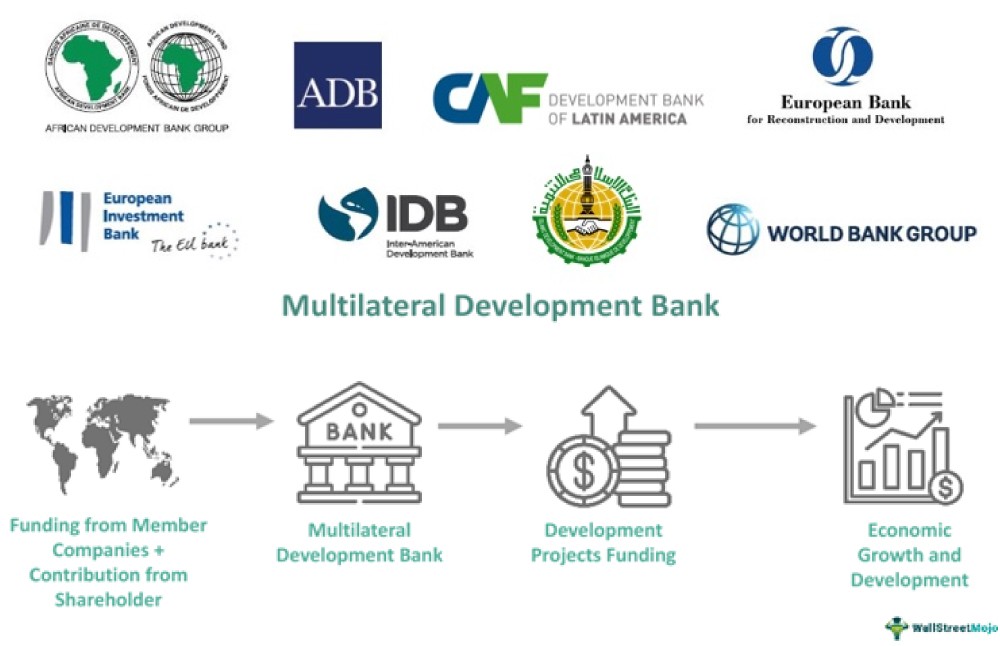
1. Utilization of G20 Principles by MDBs and DFIs
One of the pivotal aspects of the G20 New Delhi Declaration is the call for Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) and Development Financial Institutions (DFIs) to embrace and apply the G20 principles in their financing plans for urban infrastructure. This endorsement signifies a collective commitment to leveraging the principles as a cornerstone for sustainable urban development. By doing so, MDBs and DFIs can play a vital role in ensuring that urban infrastructure projects align with the principles of social inclusivity, environmental responsibility, and economic sustainability.
2. Exploration and Sharing of Experiences
Furthermore, the G20 New Delhi Declaration urges MDBs and DFIs to delve into the potential offered by these principles, incorporating them into their planning and financing strategies wherever they find applicability. This call to action represents a commitment to learning and adaptation, emphasizing the importance of sharing experiences and best practices gained from early pilot cases. Such sharing will facilitate the dissemination of knowledge, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness and impact of urban development initiatives.
3. Quality Infrastructure Investment (QII) Indicators
The declaration also acknowledges the ongoing pilot application of Quality Infrastructure Investment (QII) indicators. These indicators serve as a valuable tool for evaluating the quality and impact of infrastructure investments. Recognizing the importance of context-specific considerations, the G20 anticipates further discussions on the application of these indicators, taking into account the unique circumstances of individual countries. This approach underscores the commitment to tailor solutions to specific needs while maintaining a focus on quality and sustainability.
4. Catalyzing Disaster Risk Reduction
The G20 Presidency has assumed a leadership role in catalyzing efforts on disaster risk reduction, with a particular emphasis on early warning and early action. By prioritizing these aspects, the G20 aims to enhance the preparedness of nations and communities in the face of natural disasters. Additionally, the declaration highlights the importance of private sector investment and the exploration of innovative financing tools. This multifaceted approach acknowledges that disaster risk reduction requires a holistic strategy that involves governments, businesses, and civil society.
5. Enhancing Capabilities for Resilience
Lastly, the G20 New Delhi Declaration reiterates the continued support for enhancing the capabilities of all countries. This support extends to emerging economies, developing countries, Least Developed Countries (LDCs), and Small Island Developing States (SIDS). The objective is to empower these nations in promoting disaster and climate resilience within their infrastructure systems. This commitment to capacity-building underscores the G20’s recognition of the shared responsibility to address climate and disaster-related challenges on a global scale.
G20 Summit Insights for Urban Planning and Development
The G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration outlines the group’s priorities and commitments on a range of economic, social, and environmental issues. Key highlights include:
- Financing Cities of Tomorrow: The declaration presents a financing strategy and a compendium of innovative urban planning and financing models. It encourages stakeholders, including Development Financial Institutions and the MDBs, to explore the potential of these principles in their planning and financing of urban infrastructure.
- Inclusive Cities: The declaration outlines enablers of inclusive cities. It also mentions the customisable G20/ADB Framework on Capacity Building of Urban Administration, which is intended to guide local governments in assessing and enhancing their institutional capacity for effective public service delivery.
- Quality Infrastructure Investment (QII) Indicators: The declaration notes the ongoing pilot application of these voluntary and non-binding indicators, which could potentially guide urban development.
- Disaster Risk Reduction: The G20 Presidency has initiated efforts on disaster risk reduction, which is crucial for building resilient urban environments.
- Lifestyles for Sustainable Development: The declaration acknowledges the role of sustainable lifestyles in climate action, which can directly impact urban development and planning.
- Sustainable and Resilient Blue/Ocean-Based Economy: As part of the environmental considerations, the declaration lists a set of high-level principles for building a sustainable and resilient blue/ocean-based economy.

These points provide a comprehensive view of the G20’s approach to urban development, emphasizing financial strategies, inclusivity, infrastructure quality, disaster risk reduction, sustainable lifestyles, and environmental sustainability.

Urban Design Lab
About the Author
This is the admin account of Urban Design Lab. This account publishes articles written by team members, contributions from guest writers, and other occasional submissions. Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions or comments.
Related articles

Architecture Professional Degree Delisting: Explained
Periodic Table for Urban Design and Planning Elements


History of Urban Planning in India

Best Landscape Architecture Firms in Canada
UDL GIS
Masterclass
GIS Made Easy – Learn to Map, Analyse, and Transform Urban Futures
Session Dates
23rd-27th February 2026

Urban Design Lab
Be the part of our Network
Stay updated on workshops, design tools, and calls for collaboration
Curating the best graduate thesis project globally!

Free E-Book
From thesis to Portfolio
A Guide to Convert Academic Work into a Professional Portfolio”
Recent Posts
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
Sign up for our Newsletter
“Let’s explore the new avenues of Urban environment together “