
How Augmented Reality is Revolutionizing Public Space Design
In the age of rapid urbanization, the concept of public spaces in cities is evolving, integrating advanced technologies to foster more interactive, inclusive, and sustainable environments. Public spaces are essential to community life and urban ecosystems, and smart cities use digital technologies to improve the quality of these services. This article explores the ways in which technology is transforming the landscaping of public areas in smart cities, significantly improving social interaction and communal spaces and a different experience in urban public spaces.
Augmented Reality (AR): A Deeper Dive
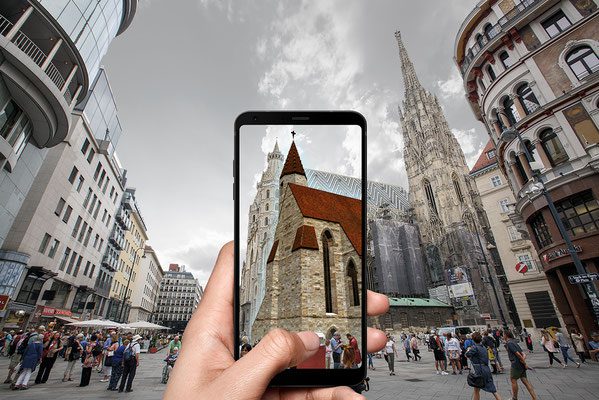
Augmented Reality (AR) represents a sophisticated interactive experience that seamlessly integrates computer-generated perceptual information with the real world. Utilizing a combination of advanced software, applications, and specialized hardware such as AR glasses, this technology superimposes digital elements—including images, videos, and three-dimensional models—onto the physical environment through devices like smartphones or tablets. The result is a synergistic interaction between the tangible and digital realms, enhancing the user’s perception and engagement with their surroundings.
Envision directing your smartphone’s camera towards a historical monument. Through AR, you could instantly access a wealth of supplementary information about the structure, such as its architectural significance, historical events associated with it, or even real-time updates on exhibitions and activities taking place within its vicinity. This enriched layer of information transforms a simple visual experience into a deeply informative and interactive encounter.

Augmented Reality: A Historical Brief
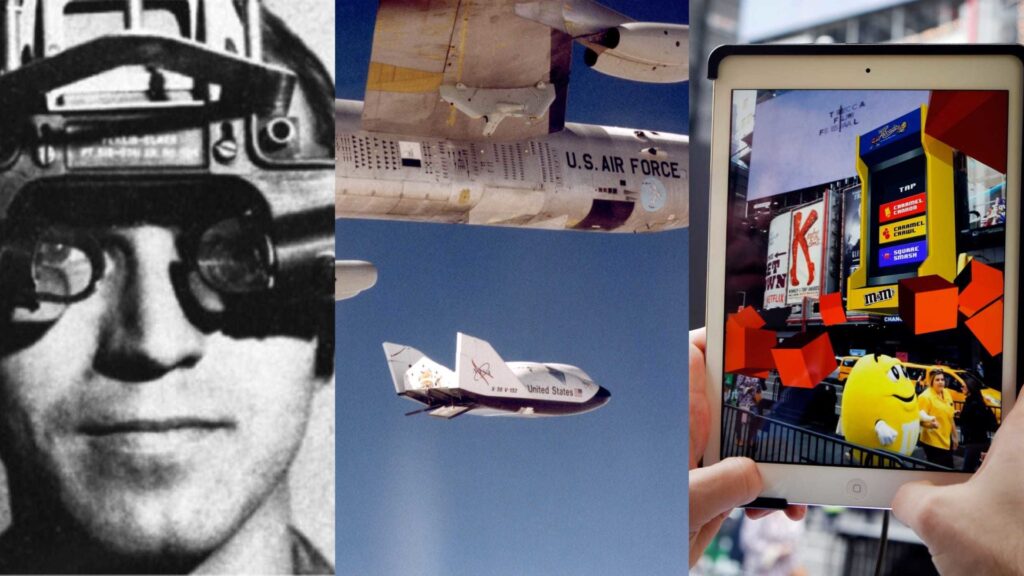
- Early Foundations in the 1960s and 1970s – Pioneering Innovations: The inception of Augmented Reality (AR) dates back to the 1960s when computer scientist Ivan Sutherland developed one of the first head-mounted display (HMD) systems, laying the groundwork for future AR technologies. The 1970s saw significant advancements with the introduction of color displays and video camera integration, which enhanced the practicality and functionality of AR systems, enabling more sophisticated overlays of digital information onto the physical world.
- Terminology and Breakthroughs in the 1990s – Defining AR: The term “augmented reality” was officially coined in the 1990s by Thomas Caudell and David Mizell at Boeing, marking a pivotal moment in the field. During this decade, Louis Rosenberg developed the Virtual Fixtures system in 1992, a groundbreaking project that allowed users to interact with virtual objects within real-world environments. This innovation demonstrated AR’s potential to enhance human capabilities in complex tasks such as surgery and remote assistance.
- Consumer Market Expansion in the 2000s and 2010s- Mainstream Adoption: The early 2000s witnessed AR gaining substantial traction in the consumer market, primarily fueled by the proliferation of smartphones and tablets. A notable milestone was the release of the Nintendo 3DS in 2011, which featured built-in AR capabilities, allowing users to interact with virtual elements in their surroundings. The mid-2010s further accelerated AR’s popularity with the launch of Pokémon Go in 2016, a mobile game that seamlessly blended virtual gameplay with real-world exploration, captivating millions globally.
- Advancements in AR Hardware and Applications in the 2010s – Enhanced Hardware Capabilities: The 2010s introduced sophisticated AR headsets such as Microsoft HoloLens and Magic Leap One, which significantly expanded the scope of AR applications. These devices enabled more immersive and interactive experiences across various sectors, including gaming, education, and professional training. The integration of these advanced headsets showcased AR’s versatility and its potential to transform user interactions with both digital and physical environments.
- Integration Across Diverse Industries in the 2020s – Broad Industrial Adoption: In the 2020s, AR has transcended its initial entertainment-focused applications, becoming integral to a wide range of industries. In healthcare, AR assists in complex surgical procedures by providing enhanced visualization and real-time data overlays. Educational institutions utilize AR to create interactive learning environments, fostering deeper understanding through immersive simulations. The manufacturing sector benefits from AR through streamlined processes and augmented workflows, while the retail industry leverages AR to enhance customer experiences by allowing consumers to visualize products in their intended settings before making purchases. These integrations underscore AR’s transformative impact, driven by continuous advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technologies.

Source: Website Link
AR vs. VR: A Quick Comparison
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are both pioneering immersive technologies that significantly enhance user experiences. While they share the common goal of altering perceptions, their methodologies and applications diverge fundamentally, catering to different user needs and scenarios.
1. Augmented Reality (AR)
Definition: Augmented Reality (AR) superimposes digital information—such as images, videos, and interactive data—onto the real-world environment. Rather than replacing the physical world, AR enhances it by adding layers of digital content that interact seamlessly with the user’s surroundings.
Experience: Users perceive the real world augmented with digital elements. This integration allows for a blended experience where virtual objects coexist and interact with the physical environment. For instance, digital annotations can provide additional context to real-world objects, enriching the user’s understanding and interaction with their environment.
Devices: AR experiences can be accessed through a variety of devices, including:
- Smartphones and Tablets: Leveraging built-in cameras and sensors to overlay digital content.
- Specialized AR Glasses: Such as Microsoft HoloLens and Magic Leap, which offer hands-free, immersive AR experiences with enhanced field-of-view and interactivity.
- Wearable Devices: Including AR-enabled smartwatches and heads-up displays integrated into eyewear.
Examples:
- Pokémon Go: A location-based game that integrates virtual creatures into real-world settings, encouraging exploration and social interaction.
- IKEA Place App: Allows users to visualize furniture in their own homes before making a purchase, enhancing the shopping experience.
- Snapchat Filters: Enhance social interactions by adding real-time digital effects to users’ faces and environments.
2. Virtual Reality (VR)
Definition: Virtual Reality (VR) creates a completely immersive, simulated environment that replaces the user’s real-world surroundings. This technology transports users into a fully virtual space, detached from their physical environment, enabling experiences that can be entirely controlled and manipulated.
Experience: Users are enveloped in a wholly virtual environment, often facilitated by head-mounted displays (HMDs) and input devices like controllers or gloves. This immersion allows for deep engagement, making users feel as though they are physically present within the virtual space. The experience is highly controlled, providing a sense of presence and interactivity that can mimic real-world scenarios or entirely fantastical settings.
Devices: VR typically requires more specialized and powerful hardware, including:
- Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs): Such as Oculus Quest, PlayStation VR, and HTC Vive, which provide high-resolution visuals and motion tracking.
- Controllers and Sensors: To enable interactive manipulation within the virtual environment.
- High-Performance Computers or Consoles: To process and render the immersive virtual experiences seamlessly.
Examples:
- Oculus Quest: A standalone VR headset offering a wide range of immersive games and applications.
- PlayStation VR: Integrates with the PlayStation gaming console to provide interactive virtual experiences.
- SteamVR: A platform that supports a variety of VR hardware, offering extensive virtual environments and gaming options.

AR in Public Space Design: Potential Applications
- Enhanced Public Art Installations: Augmented Reality (AR) transforms traditional public art by introducing dynamic and interactive elements that respond to viewer interactions or environmental factors. This evolution allows sculptures and installations to change form, color, or display additional layers of information, creating a more engaging and personalized artistic experience. Consequently, AR-enabled public art fosters a deeper connection between the artwork and the community, making art more accessible and interactive for diverse audiences.
- Innovative Educational Experiences: AR revolutionizes education within public spaces by providing immersive and interactive learning opportunities. For instance, guided tours augmented with real-time information enrich visitors’ understanding of historical sites and natural landmarks, while AR-based language learning applications offer practical, context-driven practice environments. Additionally, complex scientific concepts become more tangible through interactive simulations, making education more engaging and effective for learners of all ages.
- Transformative Urban Planning and Community Engagement: In urban planning, AR serves as a powerful visualization tool that allows stakeholders to preview proposed developments and assess their potential impact on the surrounding environment before implementation. This technology facilitates greater transparency and collaboration by enabling community members to interact with and provide feedback on planned changes, fostering a more inclusive and participatory approach to urban development. As a result, AR-driven urban planning can lead to more informed decision-making and increased public support for projects.
- Streamlined Infrastructure Maintenance and Management: AR significantly enhances the efficiency of infrastructure maintenance by overlaying real-time data and visualizations onto physical structures during inspections. This capability allows maintenance teams to identify and address issues more accurately and swiftly, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of public infrastructure. Furthermore, AR can provide detailed instructions and support for complex repairs, ensuring that maintenance work is performed correctly and safely.
- Reimagined Entertainment and Recreational Spaces: AR elevates public entertainment and recreational spaces by introducing interactive and location-based experiences that encourage exploration and social interaction. From AR-powered games that turn cityscapes into playful environments to virtual events such as concerts and festivals that blend the physical and digital realms, AR creates vibrant and dynamic public spaces. Additionally, AR-enhanced playgrounds offer innovative games and activities that stimulate creativity and physical engagement, making public recreation areas more appealing and enjoyable for all age groups.

AR in Public Space Design: Expected Benefits I
- Enhanced Engagement and Experience: AR introduces dynamic interactive elements into public spaces, making environments more engaging and memorable for users. For instance, historical landmarks can be augmented with virtual reconstructions that animate past events, allowing visitors to experience history firsthand. Additionally, parks and recreational areas can feature interactive games or educational experiences, fostering a deeper connection between individuals and their surroundings.
- Improved Accessibility: AR enhances accessibility by providing supplementary information overlays that cater to diverse user needs. Individuals with visual impairments can benefit from AR features that highlight accessible routes and offer descriptive audio cues about landmarks. Moreover, real-time language translation capabilities make public spaces more inclusive, enabling visitors from various cultural backgrounds to navigate and enjoy these areas with ease.
- Economic Benefits: AR-enhanced public spaces attract tourists by offering unique and immersive experiences that differentiate them from traditional attractions. This influx of visitors can stimulate local economies through increased spending on tourism-related services such as dining, shopping, and accommodation. Furthermore, AR can spotlight local businesses and attractions, driving foot traffic and providing businesses with innovative marketing opportunities to reach a broader audience.
- Educational Opportunities: AR serves as a powerful educational tool within public spaces, facilitating interactive and contextual learning experiences. Guided AR tours of historical sites or natural landmarks can provide in-depth information and engaging narratives that deepen visitors’ understanding and appreciation. Additionally, AR simulations can simplify complex scientific concepts, making education more accessible and enjoyable for learners of all ages.
- Community Building: AR fosters a sense of community by creating shared interactive experiences that encourage social interaction and collaboration. Location-based AR games and events can bring people together, promoting exploration and teamwork within public spaces. Moreover, AR applications can involve residents in the urban planning process by allowing them to visualize and interact with proposed changes, thereby fostering a collective sense of ownership and investment in the development of their environment.

AR in Public Space Design: Expected Benefits II
While Augmented Reality (AR) offers substantial enhancements to public spaces, its implementation presents several challenges that must be thoughtfully addressed to ensure successful integration.
- Enhanced Engagement and Experience: AR introduces dynamic interactive elements into public spaces, making environments more engaging and memorable. For example, historical landmarks can be augmented with virtual reconstructions that animate past events, allowing visitors to experience history firsthand. Additionally, parks and recreational areas can feature interactive games or educational experiences, fostering a deeper connection between individuals and their surroundings.
- Improved Accessibility: AR enhances accessibility by providing supplementary information overlays that cater to diverse user needs. Individuals with visual impairments can benefit from AR features that highlight accessible routes and offer descriptive audio cues about landmarks. Moreover, real-time language translation capabilities make public spaces more inclusive, enabling visitors from various cultural backgrounds to navigate and enjoy these areas with ease.
- Economic Benefits: AR-enhanced public spaces attract tourists by offering unique and immersive experiences that differentiate them from traditional attractions. This influx of visitors can stimulate local economies through increased spending on tourism-related services such as dining, shopping, and accommodation. Furthermore, AR can spotlight local businesses and attractions, driving foot traffic and providing businesses with innovative marketing opportunities to reach a broader audience.
- Educational Opportunities: AR serves as a powerful educational tool within public spaces, facilitating interactive and contextual learning experiences. Guided AR tours of historical sites or natural landmarks can provide in-depth information and engaging narratives that deepen visitors’ understanding and appreciation. Additionally, AR simulations can simplify complex scientific concepts, making education more accessible and enjoyable for learners of all ages.
- Community Building and Environmental Benefits: AR fosters a sense of community by creating shared interactive experiences that encourage social interaction and collaboration. Location-based AR games and events can bring people together, promoting exploration and teamwork within public spaces. Moreover, AR promotes environmental awareness and conservation through sustainability education and support for conservation efforts. AR overlays can highlight eco-friendly features in public spaces or provide information on local wildlife, enhancing public understanding and involvement in environmental protection.

AR in Public Space Design: Challenges and Considerations
While Augmented Reality (AR) offers substantial enhancements to public spaces, its implementation presents several challenges that must be thoughtfully addressed to ensure successful integration.
- Technical Challenges: AR applications are often hindered by hardware limitations such as insufficient performance, limited battery life, and discomfort during prolonged use. Additionally, reliable network connectivity is essential for real-time data processing, which can be problematic in densely populated or remote areas. Integrating AR with existing infrastructure like signage and lighting systems also requires significant effort and coordination.
- User Experience Challenges: The deployment of AR in public spaces raises important privacy concerns, as data collection and surveillance capabilities may deter user engagement. Ensuring accessibility for all individuals, regardless of age, ability, or socioeconomic status, remains a significant hurdle. Moreover, an overload of AR information can overwhelm users, potentially leading to a negative experience and reduced interaction with the technology.
- Social and Cultural Considerations: AR applications must be designed with cultural sensitivity to respect and reflect the diverse traditions and customs of the communities they serve. Inappropriate or insensitive content can lead to misunderstandings and social friction, undermining the technology’s benefits. Engaging local communities and cultural experts during the design process is crucial to creating respectful and meaningful AR experiences.
- Environmental Considerations: The energy consumption associated with AR devices and infrastructure can contribute to the environmental footprint of public spaces, posing sustainability challenges. Additionally, excessive or poorly designed AR overlays may result in visual pollution, detracting from the aesthetic appeal of urban environments. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and thoughtful design practices are essential to minimize the environmental impact of AR integrations.

Conclusion
As AR technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and exciting applications in public space design. By leveraging the power of AR, we can transform our cities into more immersive, engaging, and sustainable places for everyone.
But the challenges and considerations will be crucial for the successful implementation of AR in public space design. And By carefully considering the technical, user experience, social, cultural, and environmental factors, we can create AR experiences that benefit everyone and enhance the quality of our public spaces.
References
- https://www.thedigitalspeaker.com/augmenting-urban-landscapes-ar-generative-ai-change-city/
- https://artificialpaintings.com/blog/2024/06/21/digital-art-in-public-spaces-transforming-urban-environments/
- https://www.uxstudioteam.com/ux-blog/augmented-reality
- https://www.blippar.com/blog/2018/06/08/history-augmented-reality
- https://spectrum.ieee.org/augmented-reality-for-public-spaces
- https://www.darfdesign.com/blog/7-ways-augmented-reality-will-revolutionise-our-cities

Mirna George
About the Author
Mirna George is a senior Architecture Student at Faculty of engineering Ain Shams University . Worked on various projects during her academic past years such as hotel , community center , luxurious compounds and mixed use building . Passionate in urban designs , modern developments and learning architecture aspects . Participated in many architectural competitions to develop her architecture skills . Also volunteered in many organizations and become one of their high board .
Related articles


William H. Whyte public space theory

Model Making Techniques for Urban Design and Landscape



UDL GIS
Masterclass
GIS Made Easy – Learn to Map, Analyse, and Transform Urban Futures
Session Dates
23rd-27th February 2026

Urban Design Lab
Be the part of our Network
Stay updated on workshops, design tools, and calls for collaboration
Curating the best graduate thesis project globally!

Free E-Book
From thesis to Portfolio
A Guide to Convert Academic Work into a Professional Portfolio”
Recent Posts
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
Sign up for our Newsletter
“Let’s explore the new avenues of Urban environment together “









































One Comment