7 Elements of Urban Design: Creating Vibrant and Livable Cities

What is Urban Design?
Urban design is a crucial component of city planning that entails modifying the physical characteristics of cities, towns, and villages to produce aesthetically pleasing, practical, and environmentally friendly urban settings. It is the art of making places that not only satiate the requirements of the inhabitants and guests, but also inspire and improve their quality of life. Architecture, engineering, landscape design, and public policy are just a few of the many disciplines that are used into urban design. At its core, it is a collaborative effort that needs the advice of professionals and stakeholders to create spaces that are both functional and visually beautiful. Understanding the seven basic components of urban design is necessary for anybody involved in the planning and development of urban settings because they play a significant role in producing successful urban places.
Elements of Urban Design
The goal of urban design is to create functional, attractive, and sustainable urban environments. There are seven essential elements of urban design that are crucial for creating successful urban spaces. These elements are:

1. Streetscape
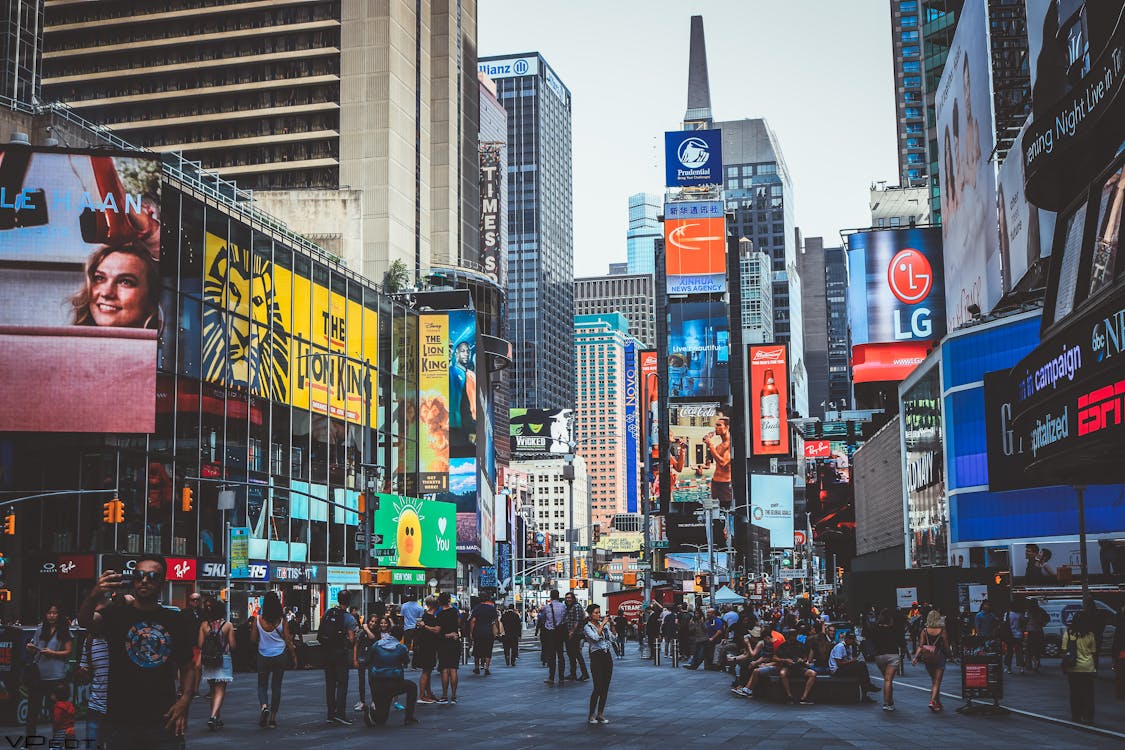
The term “streetscape” defines the visible and tangible components that together make up a street’s overall appearance. It includes a variety of architectural components that enhance a street’s usability and aesthetic appeal, such as street furniture, lighting, planting, pavement materials, and signage. A well-planned streetscape can produce an inviting and appealing atmosphere that motivates visitors to hang out on the sidewalk and interact with the neighbourhood. A well-designed streetscape can increase a street’s utility in addition to its aesthetic appeal by including welcoming seats, sufficient lighting, understandable signs, and well-maintained infrastructure. The quality of life of both inhabitants and visitors can therefore be significantly improved by investing in a smart and integrated streetscape design. Some examples of well-designed streetscapes include:
New York's Times Square, which has vibrant LED billboards and street performers

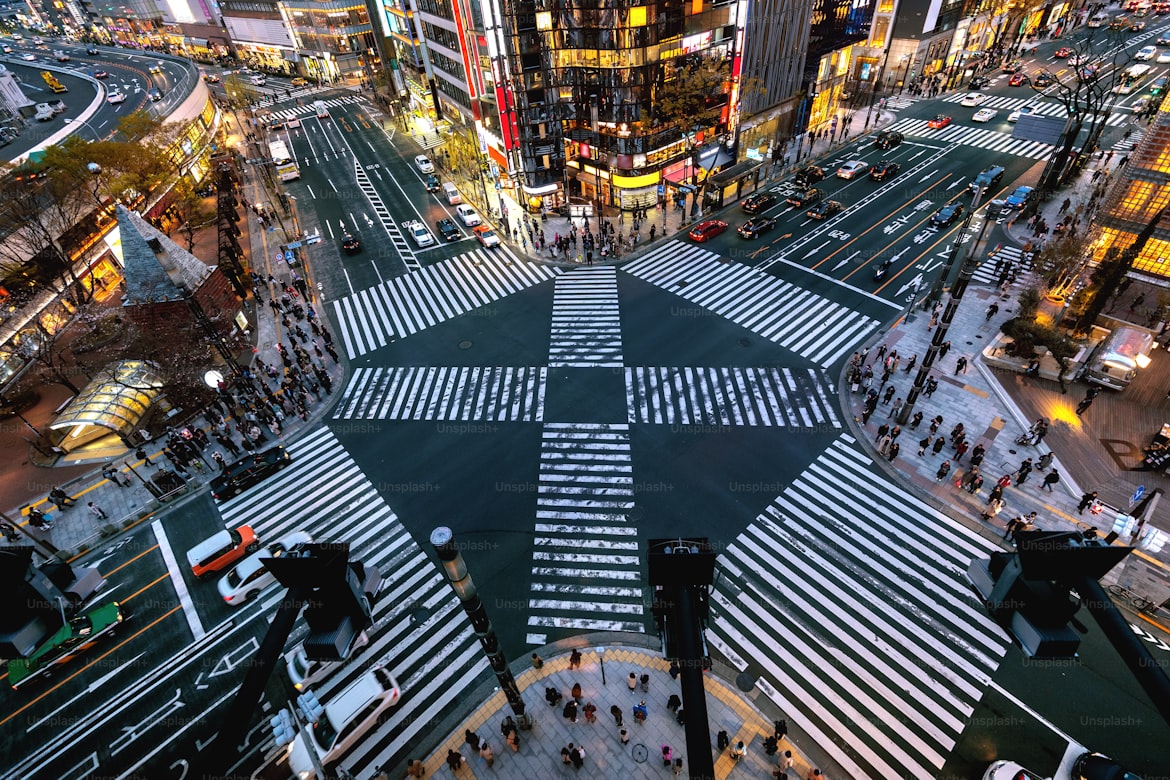
Tokyo's Shibuya Crossing, which has large pedestrian crossings and neon signs.

2. Public Spaces:
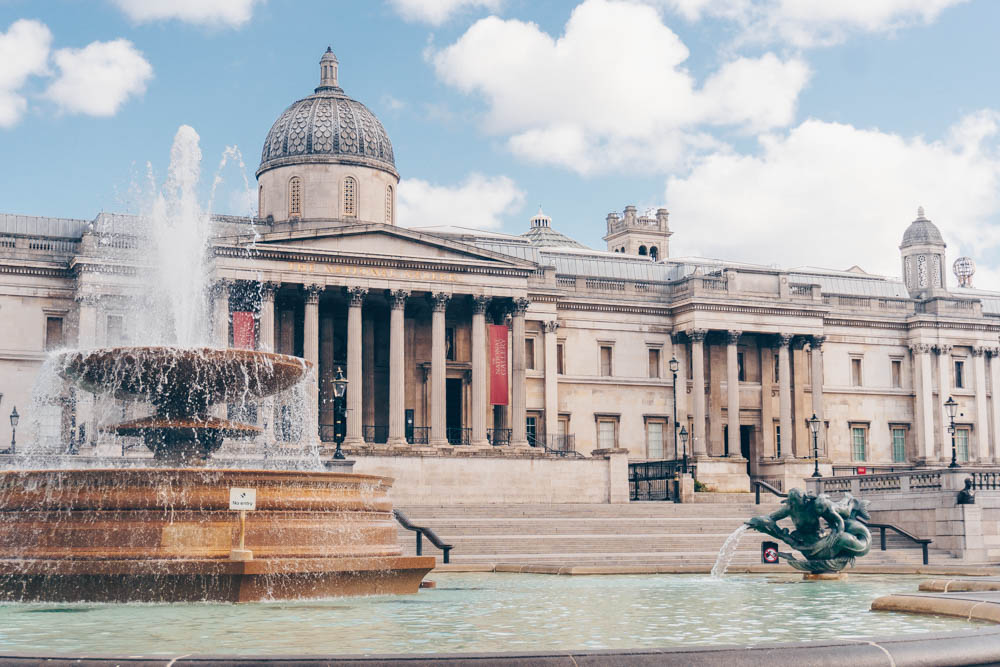
Public spaces are defined as places in urban settings where people can congregate and interact with one another. Parks, public plazas, squares, and other open spaces are included in these locations. In order to encourage social contact and community formation in metropolitan environments, well-designed public spaces are crucial. They give people from all cultures and backgrounds a place to meet, exchange stories, and develop a sense of community. By offering chances for leisure, relaxation, and appreciation of nature, public places can also encourage physical exercise, mental health, and general well-being. Public spaces can improve the social, economic, and environmental life of metropolitan communities when they are thoughtfully planned and efficiently administered. As a result, spending money on the development and upkeep of public areas is essential for creating thriving, healthy, and sustainable cities.
Trafalgar Square in London, which has fountains, statues, and public art.

3. Building Design:
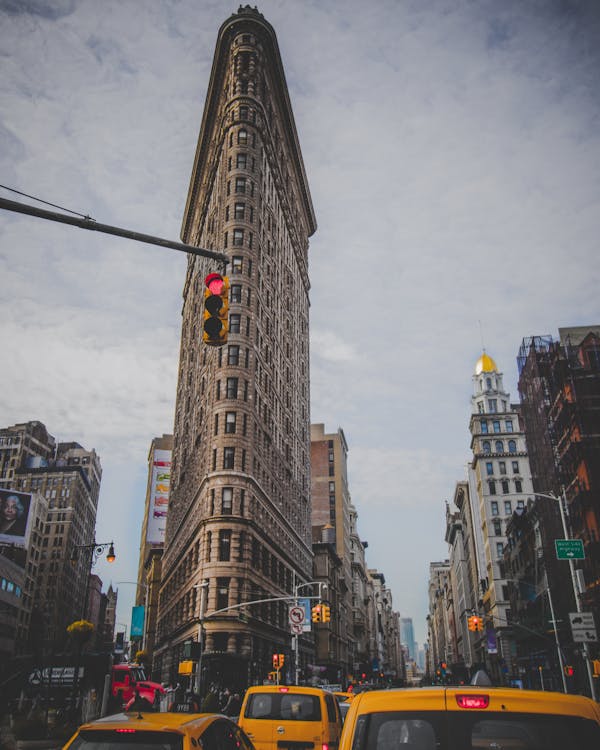
Building design includes both the architecture and design of specific buildings found in urban settings. It is an essential component of urban design that has a big impact on the general feel and standard of a street or neighbourhood. In addition to improving the aesthetic appeal of its surroundings, a well-designed building can also improve the built environment’s use and sustainability. An array of elements, such as the site context, building orientation, energy efficiency, and accessibility, are taken into account in effective building design. Buildings with sustainable design elements like green roofs, passive solar heating, and rainwater harvesting systems are some examples of well-designed structures. They might also have creative and appealing design aspects that accentuate the personality and uniqueness of their surroundings, such as spectacular facades, vivid colors, and unusual shapes. In the end, spending money on high-quality building design can significantly improve the livability and vibrancy of metropolitan areas, assisting in the development of prosperous and sustainable communities.
The Flatiron Building in New York City, which has a triangular shape and a Beaux-Arts façade.

4. Accessibility:
Accessibility describes how easily and conveniently people can travel around a city. This includes a variety of components that promote mobility in metropolitan settings, including sidewalks, bike lanes, and other infrastructure. The functionality and livability of cities are directly impacted by accessibility, making it a crucial element of urban design. Cities that place a high priority on accessibility are more likely to attract both residents and tourists. Because accessible transportation options can help reduce dependency on vehicles and encourage active and healthy lifestyles, they are also more likely to be sustainable and egalitarian. One strategy to increase accessibility in cities is to invest in public transportation, increase the number of bike lanes and pedestrian walkways, and enhance the quality and security of sidewalks and other infrastructure. Cities can build more vibrant, interconnected communities that benefit all citizens by giving accessibility a higher priority in urban planning.
Amsterdam, which has an extensive network of bike lanes and is considered one of the most bike-friendly cities in the world.
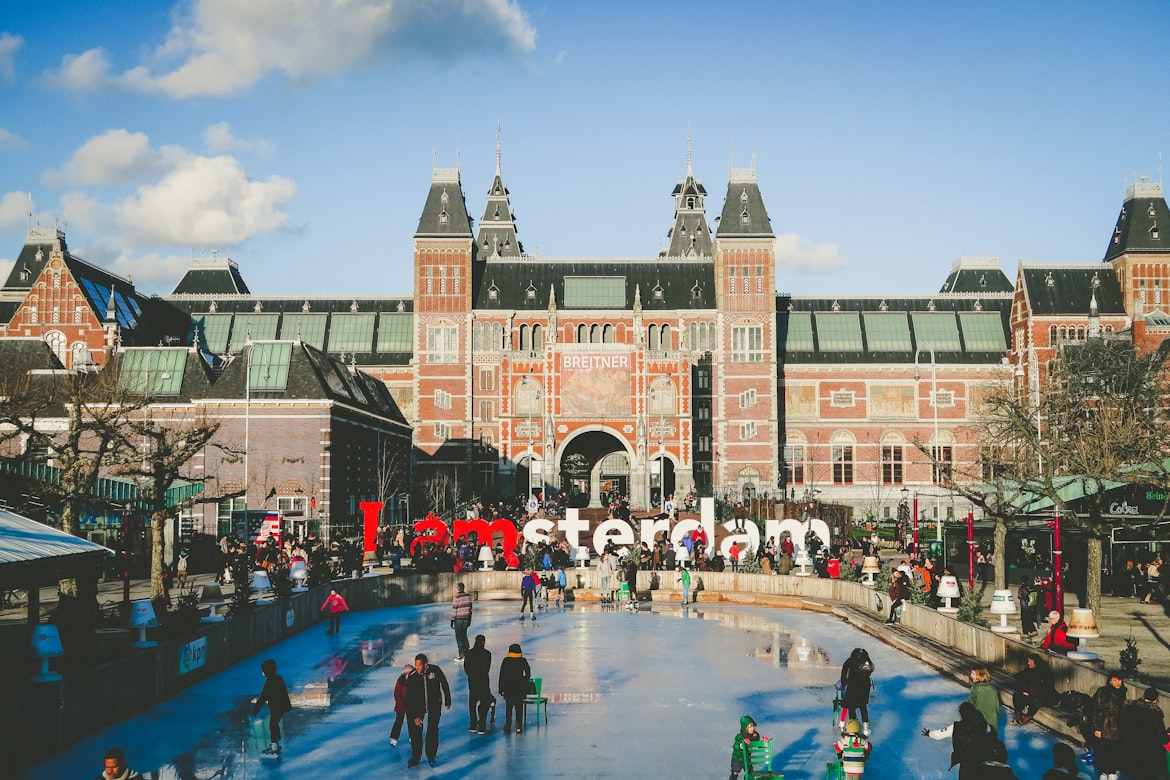

5. Sustainability:
Urban design must include sustainability, which refers to a city’s ability to accommodate its citizens’ requirements without jeopardising the ability of future generations to do the same. Planning and building cities sustainably means taking into account their social, economic, and environmental impacts. This includes a variety of components like the use of green spaces, renewable energy sources, and energy-efficient structures. To build habitable, resilient communities that can adjust to changing conditions and lessen the effects of climate change, sustainable urban design is crucial. By giving priority to the needs of vulnerable groups and minimising environmental and social inequities, it also encourages the development of more equitable and inclusive communities. In order to achieve sustainability in urban design, a comprehensive strategy that takes into account everything from waste management to building design and energy use is necessary. Cities can build more resilient, just, and prosperous communities that are beneficial to all citizens by putting sustainability first in urban planning.
Copenhagen, which has a goal of becoming carbon-neutral by 2025 and has invested in wind power and sustainable transportation options.
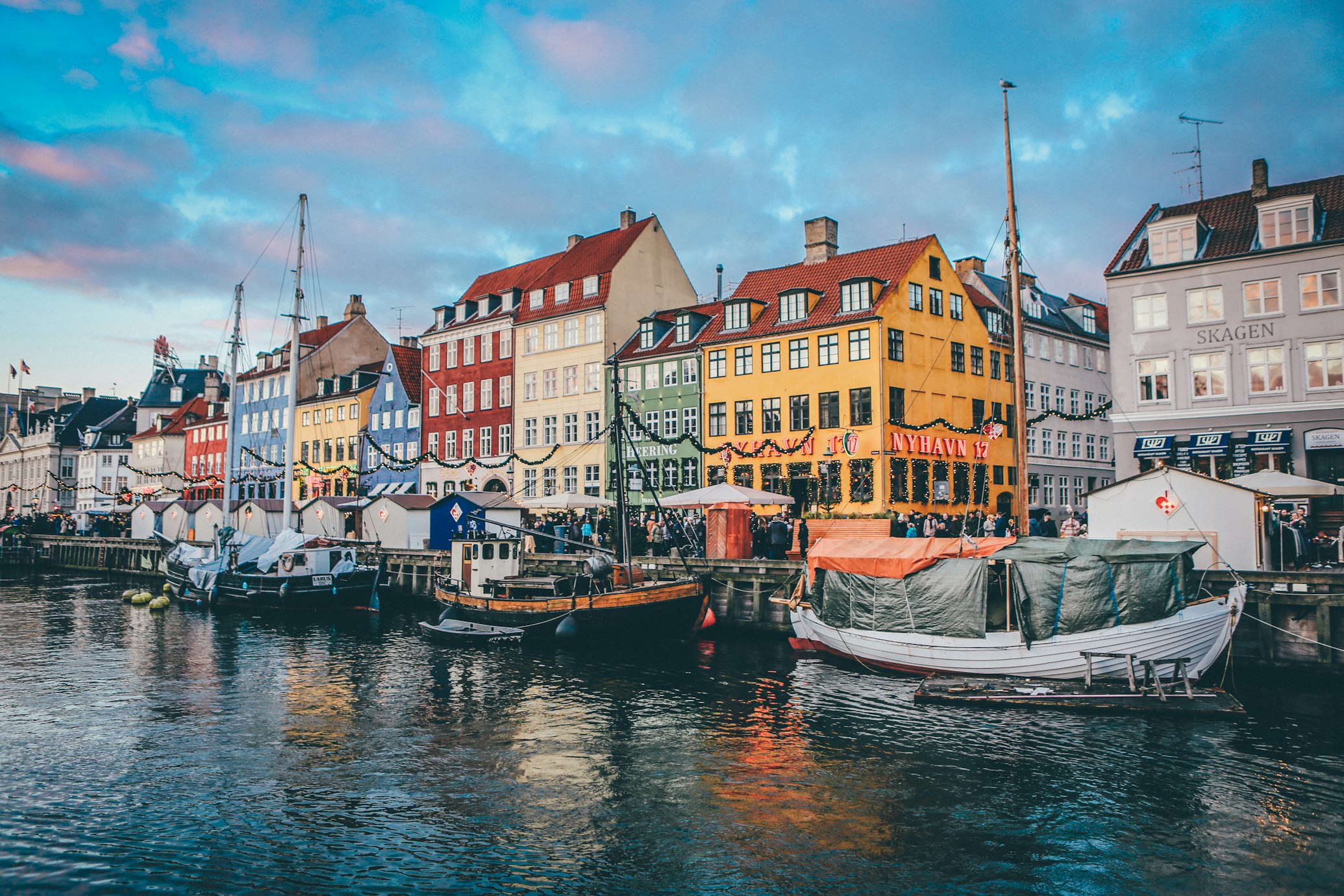

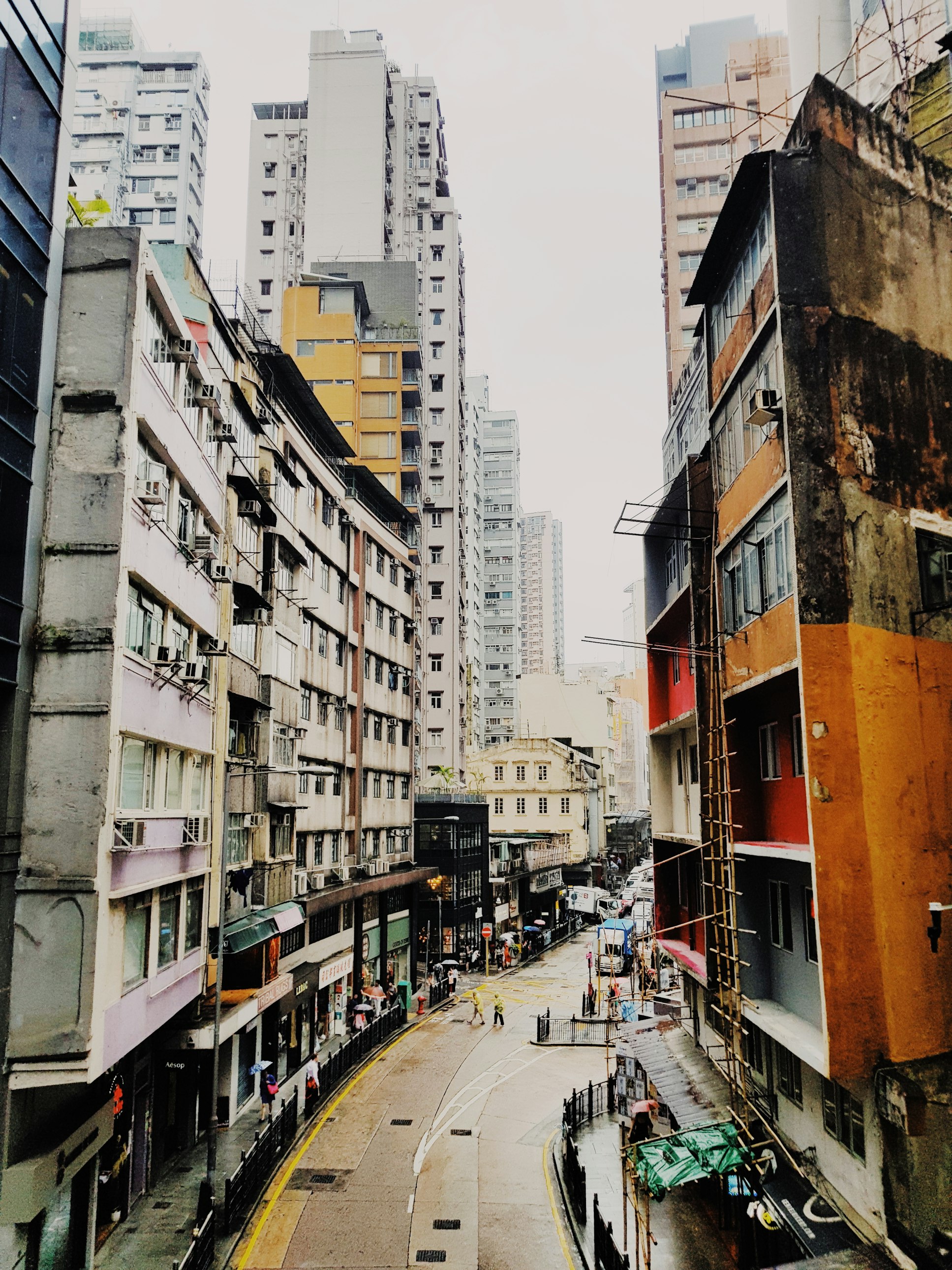
6. Density:
Density is an essential consideration in urban design, as it refers to the number of people living in a specific area. Greater access to facilities like stores, public transit, and community services, as well as more effective resource usage, are just a few advantages of higher density. However, it can also result in issues like backed-up traffic, crowded living spaces, and reduced privacy. To develop livable, sustainable, and fair communities, urban planners must carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of density. Urban designers may maximise the positive effects of density while minimising its negative effects by supporting mixed-use development and pedestrian-friendly streetscapes. Incorporating green spaces and public gathering places can also serve to lessen the drawbacks of high-density living by fostering chances for recreation and social contact. Designing for density ultimately necessitates a comprehensive strategy that promotes livability and sustainability for all people while taking into account the particular demands and preferences of various communities.
Hong Kong, which is one of the most densely populated cities in the world and has a comprehensive public transportation system.

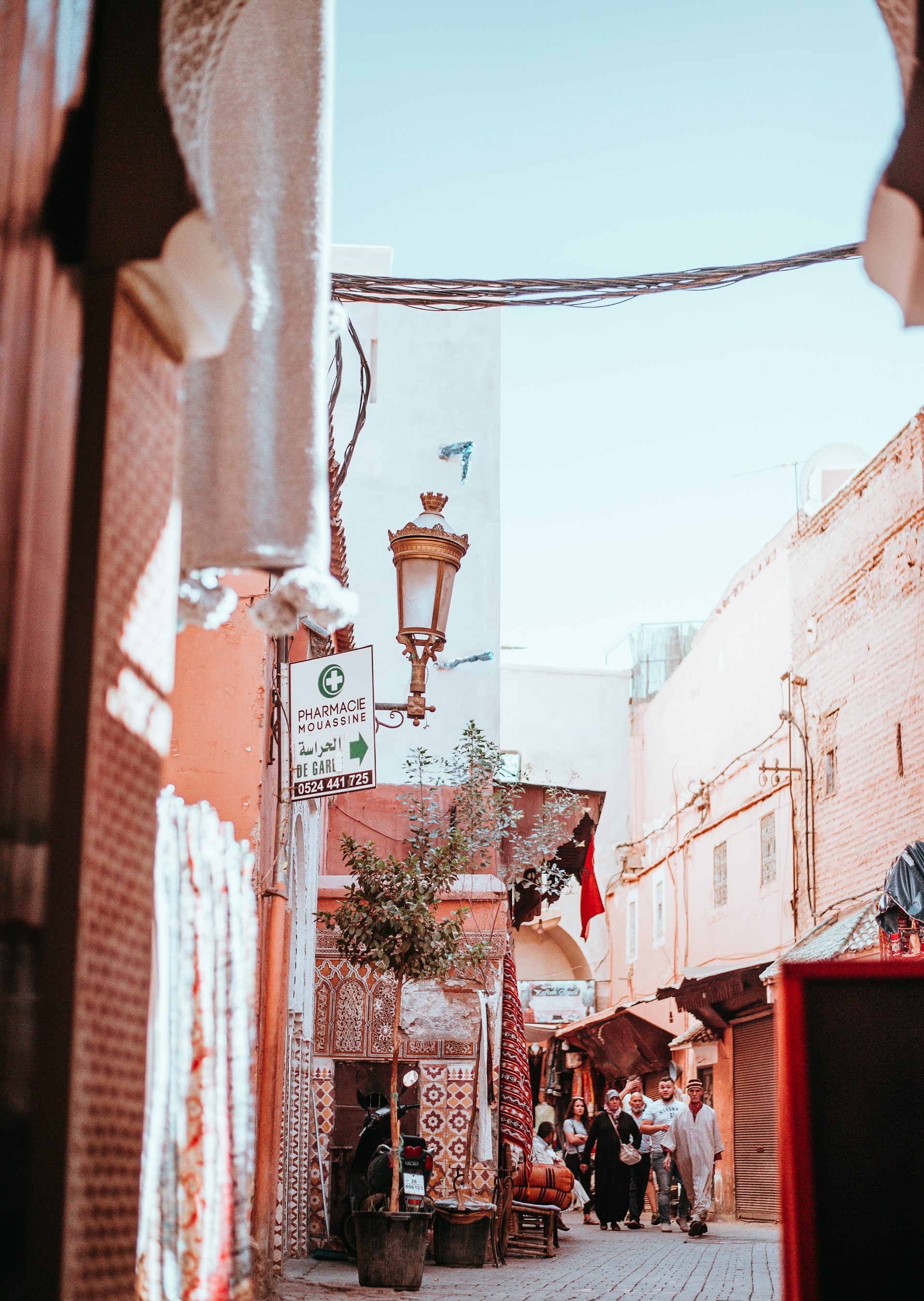
7. Identity:
In urban design, creating a sense of identity is crucial to the success of a city or neighborhood. Identity refers to the unique character and personality of a place that sets it apart from others. A strong and distinctive identity can make a city more attractive and memorable, helping to draw visitors and investment, and foster community pride. Identity can be created through various means, including architecture, public art, and historical preservation. The use of local materials, traditional building styles, and indigenous plants can also contribute to a place’s identity. Urban designers can work to reinforce and enhance a place’s identity by celebrating its cultural heritage, supporting local businesses and events, and creating memorable public spaces. By creating a strong sense of identity, urban designers can foster a sense of community and pride, and create a lasting legacy that future generations can enjoy.
Marrakech, Morocco, which is known for its vibrant markets, intricate tilework, and ornate architecture.

In conclusion, urban design plays a crucial role in shaping our cities, towns, and villages. By considering the seven essential elements of urban design, we can create functional, attractive, and sustainable urban environments that promote social interaction, community building, and accessibility. From the design of individual buildings to the density of a particular area, each element has a significant impact on the overall character of a city or neighbourhood. By prioritizing these elements in urban planning and design, we can create cities that are both livable and memorable for current and future generations.

Urban Design Lab
About the Author
This is the admin account of Urban Design Lab. This account publishes articles written by team members, contributions from guest writers, and other occasional submissions. Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions or comments.
Related articles

Architecture Professional Degree Delisting: Explained
Periodic Table for Urban Design and Planning Elements


History of Urban Planning in India

Kim Dovey: Leading Theories on Informal Cities and Urban Assemblage
UDL GIS
Masterclass
GIS Made Easy – Learn to Map, Analyse, and Transform Urban Futures
Session Dates
23rd-27th February 2026

Urban Design Lab
Be the part of our Network
Stay updated on workshops, design tools, and calls for collaboration
Curating the best graduate thesis project globally!

Free E-Book
From thesis to Portfolio
A Guide to Convert Academic Work into a Professional Portfolio”
Recent Posts
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
Sign up for our Newsletter
“Let’s explore the new avenues of Urban environment together “