Software Tools for Quantitative Research in Urban Planning

Quantitative research is essential to comprehending, assessing, and enhancing urban settings in the dynamic field of urban planning and design. Numerous software programs have been created to help urban planners, designers, and researchers with their data processing, visualization, and simulation duties in order to facilitate such research projects. This article delves into the prominent software tools used in the field of quantitative research in urban planning and design.
1. STATA:
STATA is a powerful statistical tool that stands out in the complex investigation of urban dynamics. Urban planners and researchers now have a powerful toolkit to analyze the many layers of socioeconomic and demographic data thanks to this durable software. A tapestry of insights is created as they delve deeply into the complexities of urban settings, with each thread exposing essential knowledge that serves as the basis for wise policy and tactical choices.
STATA turns out to be a crucial tool in the dynamic world of urban areas, where populations fluctuate and patterns change quickly. Professionals can decipher the complex patterns that characterize cities, towns, and metropolitan areas because to its analytical prowess. STATA assists in the extraction of significant insights that offer a comprehensive view of urban civilizations by painstakingly crunching numbers and extrapolating trends.

2. SPSS:
The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), a vital instrument that is crucial in revealing the complex layers of urban dynamics, is at the forefront of urban data analysis. With its extensive set of statistical analytic tools, SPSS equips researchers to wade through the immense ocean of urban data, shedding light on obscured trends, revealing correlations, and identifying patterns that lie beneath the surface. Urban planners and academics have a magnifying glass through which to examine the intricate interaction of socio-economic elements, demographic changes, and spatial dynamics that define modern cities thanks to its skill in quantitative analysis, which turns raw data into practical insights.
Evidence-based decisions dominate in the world of urban planning and policy-making, and SPSS is a reliable ally in this pursuit. It extracts information that aids urban stakeholders in developing successful plans by carefully and systematically filtering through big datasets. With the aid of SPSS, researchers may reveal the hidden meaning in the data, illuminating issues like unequal income distribution, unequal access to basic services, and changes in population density. These discoveries give urban planners a framework on which to construct adaptable policies that address the particular requirements and difficulties of urban populations, guiding cities toward sustainable growth and improved quality of life.
3. R:
R develops as a fierce competitor in the field of in-depth statistical analysis, providing a programming language and environment designed for the complexities of advanced data investigation. In order to start on a journey of custom analyses and data visualizations, urban researchers use the power of R. These analyses and data visualizations unravel hidden revelations inside the intricate tapestries of urban datasets.
R, a flexible programming language, meets the complex requirements of researchers exploring urban dynamics. Because of its adaptability, specialists can create specialized studies that answer the precise issues raised by the urban environment. Within the constraints of R’s environment, researchers can modify data, apply sophisticated statistical models, and develop customized algorithms. When dealing with the varied nature of urban data, which frequently requires novel approaches to unearth insightful information, this adaptability becomes important.
4. MATLAB
The mathematical engine in MATLAB equips academics to precisely address real-world urban concerns. Researchers can foresee trends, study the effects of policy choices, and decipher complex cause-and-effect linkages through numerical calculations. Urban stakeholders are guided toward evidence-based decisions that drive cities toward sustainability, efficiency, and resilience by the capacity to alter complex mathematical equations within the MATLAB environment. MATLAB serves as a beacon in the constantly changing field of urban planning and research, illuminating the way to a deeper comprehension of urban complexity and aiding the development of efficient methods.
Researchers can experiment with various scenarios and variables by building complex models that capture the multiple relationships inside urban systems, whether it be traffic flow, energy usage, or population dynamics. These simulations allow decision-makers a virtual testing ground to assess plans before to execution, giving them a glimpse into the prospective outcomes of various urban actions.
5. Tableau:
Data abounds in the urban environment, most of it complicated and diverse. The strength of Tableau resides in its capacity to take these unprocessed data bits and transform them into engaging visual stories. Urban experts are able to create visualizations that go beyond conventional static representations using a variety of customisable charts, graphs, and maps. These interactive graphics give data alive and let decision-makers explore the subtleties of urban dynamics while quickly seeing correlations, outliers, and potential action areas.
Tableau serves as a transformative lens in the hands of urban designers and planners, illuminating the essence of data in an understandable way. Stakeholders, from politicians to the general public, can interact with these visualizations and quickly comprehend the pulse of a city. Tableau gives urban professionals the tools they need to tell engrossing tales that capture the nuances of urban life, whether they are demonstrating changes in population distribution, examining travel patterns, or monitoring changes in urban infrastructure. In the end, Tableau excels as a conduit in the field of data-driven decision-making, bridging the gap between unprocessed data and knowledgeable urban strategies.
6. SPatial Analysis and Decision Assistance (SPADA):
SPADA emerges as a key resource in the dynamic world of urban planning, where spatial considerations are crucial. This software provides a specialized toolkit that allows experts to analyze spatial data with unmatched precision. Urban planners and academics may decipher the intricate interplay of geographic variables, from land use patterns and transportation networks to population densities and environmental aspects, by utilizing cutting-edge spatial analytics and visualization approaches.
The capabilities of SPADA go beyond those of traditional data analysis. It enables experts to estimate future spatial patterns, simulate scenarios, and evaluate the potential effects of planning measures. Urban stakeholders can make well-informed decisions that are based on the geographical reality of a city or region by using this dynamic method. Thus, SPADA acts as a compass, improving the urban planning process by shedding light on the intricate spatial relationships that determine the structure of cities and boosting the effectiveness of plans intended to create thriving, useful, and resilient urban places.
7. TransCAD
Urban transportation networks act as veins that pulse across the urban environment, affecting the movement of people, products, and ideas. Professionals may thoroughly study these networks using TransCAD’s specialized features, precisely charting out paths, nodes, and connections. Urban planners are able to identify congestion hotspots, accessibility gaps, and prospective improvement locations through thorough spatial analysis, enabling them to make well-informed decisions that optimize transportation infrastructure.
TransCAD’s capacity to predict travel patterns and simulate how people and vehicles move across urban environments is at the heart of its usefulness. TransCAD makes it easier to create dynamic scenarios by extrapolating data on commuter habits, congested areas, and journey times. With the use of these simulations, planners can investigate possible interventions—such as the deployment of congestion pricing or the addition of additional public transit routes—and weigh their potential effects prior to their implementation.
8. SimCity
SimCity has a significant place in urban studies despite not being created specifically for experts. Through providing a useful platform for users to engage in urban modeling and experimentation, this simulation game goes beyond its entertainment intent. SimCity offers a distinctive platform for understanding prospective urban outcomes by enabling players to alter urban dynamics, test various planning scenarios, and observe the effects of their decisions.
SimCity’s digital environments replicate the urban complexity found in real life and let users create, construct, and oversee their own cities. Players are encouraged to consider the complex problems that urban planners and policymakers deal with on a regular basis in this interactive environment. Users may see how their choices in zoning, infrastructure, and public services affect the health and development of their virtual metropolises because to the simulation’s responsive mechanics.

9. Excel
Excel, a ubiquitous tool in diverse domains, also finds a crucial role in the realm of urban planning. Renowned for its prowess in organizing, analyzing, and visualizing data, Excel serves as an indispensable companion for urban professionals, aiding them in managing and comprehending intricate datasets.
In the intricate world of urban planning, data lies at the core of informed decision-making. Excel’s versatile capabilities empower professionals to efficiently organize and structure complex datasets, transforming raw information into a coherent framework. By utilizing features like spreadsheets and tables, urban planners can categorize data related to population demographics, land use, infrastructure, and more, allowing for streamlined access and management.
10. Space Syntax Software
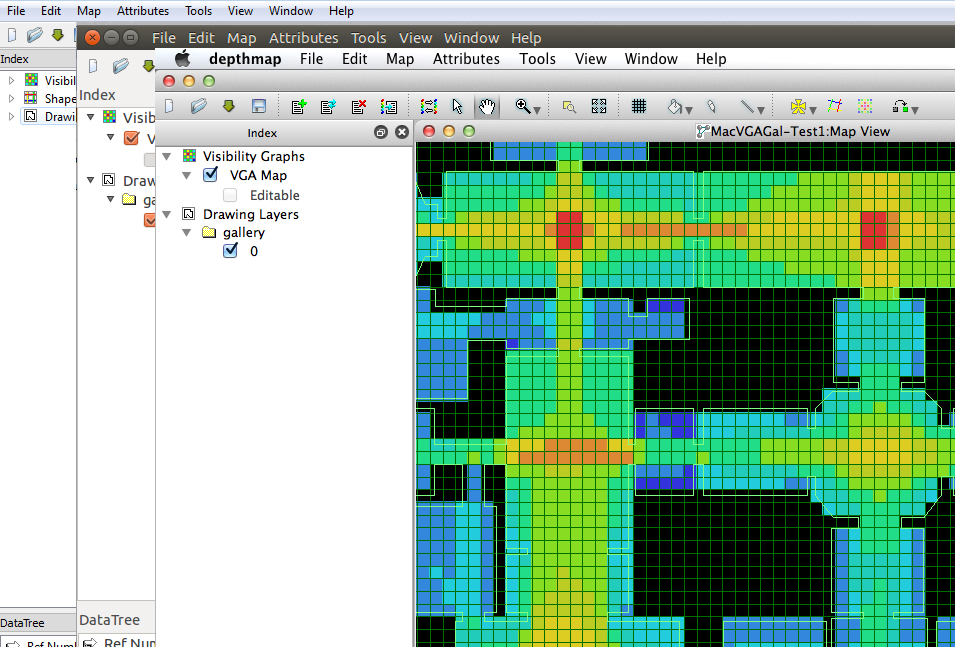
For urban professionals looking to understand the intricate interplay of spatial relationships in urban contexts, DepthMap and the Space Syntax Toolkit are priceless resources. These tools decipher the patterns of movement and flow that characterize urban layouts using complex algorithms and cutting-edge spatial analytic techniques. Urban designers and planners can identify the dynamics that influence people’s behavior in cities by measuring the connectivity between various locations and the accessibility of particular spaces.
One of Space Syntax Software’s most important achievements is its capacity to anticipate how people would interact with metropolitan environments. The positioning of facilities, open areas, and transportation hubs can be made more effective by planners by understanding the spatial configurations that affect pedestrian flow. These tools also assist in locating possible congestion sites, assisting in making choices that promote effective traffic circulation and improve the general functionality of urban environments.
11. Pedestrian and Evacuation Dynamics (PRED)
Pedestrian and Evacuation Dynamics (PRED) emerges as a significant tool for prioritizing convenience and safety in urban contexts. In order to ensure that designs are fundamentally sensitive of the well-being and convenience of pedestrians, this program equips specialists to simulate pedestrian movement within metropolitan settings.
The movement of pedestrians is a key factor in developing inclusive and practical environments in the field of urban planning and design. PRED provides experts with a specialized platform to model and analyze pedestrian dynamics, enabling them to picture how people move through streets, plazas, and public spaces. PRED enables planners and designers to examine variables including traffic, accessibility, and potential bottlenecks, hence improving designs to improve the entire pedestrian experience.

12. UrbanFootprint
UrbanFootprint excels in evaluating land use patterns comprehensively in the effort to create dynamic and resilient cities. Urban planners are able to get insight into the potential balance between various land uses by carefully examining the allocation of spaces for residential, commercial, and recreational activities. By maximizing the use of existing space, encouraging mixed-use neighborhoods, and reducing urban sprawl, this research opens the way for more effective and coherent urban settings.
A crucial component of urban functionality, infrastructure assessment is another area where UrbanFootprint excels. With the aid of this software, experts may evaluate how urban life is affected by transportation systems, utilities, and public services. Planners can anticipate future bottlenecks, create sustainable transit options, and guarantee that basic services are available across the city by predicting how infrastructure components will interact.

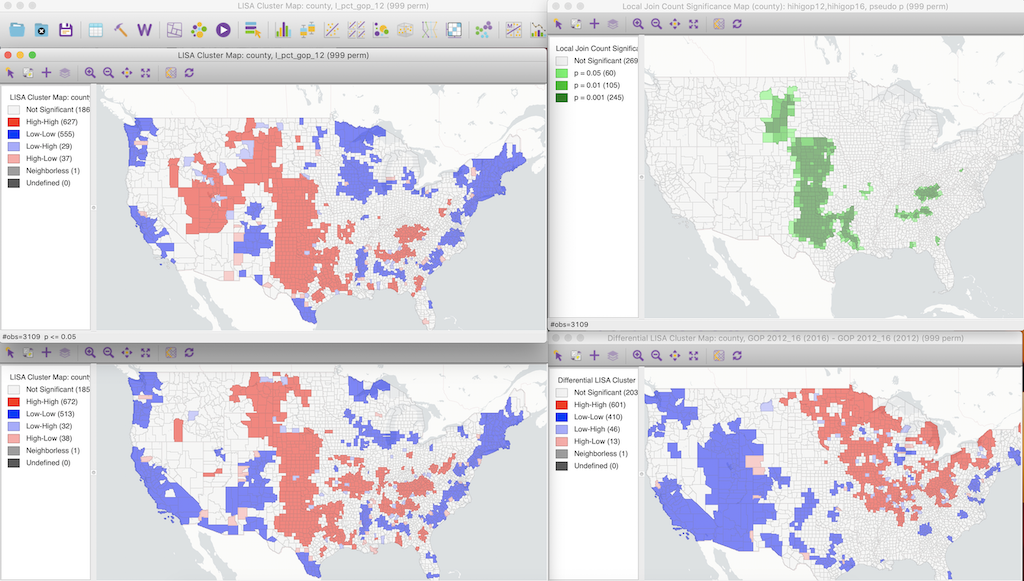
13. GeoDA
GeoDA is a reliable ally for geospatial analysis. With the use of this software, researchers may decipher spatial correlations, trends, and variations as they delve into the intricate fabric of urban surroundings. GeoDA is essential in assisting with well-informed planning decisions by shedding light on the geographic characteristics of urban settings.
Researchers can dig below the surface and uncover hidden insights by utilizing GeoDA’s capabilities. Spatial autocorrelation, hotspot analysis, and cluster discovery may all be explored using the software’s features, which helps us better understand how various factors interact in urban settings. This information acts as a compass, pointing planners in the direction of identifying areas that need for focused interventions or policy changes.
14. AIMSUN
The importance of AIMSUN resides in its capacity to analyze and model complex transportation systems. Urban mobility is essential to cities, and AIMSUN’s sophisticated tools enable experts to build intricate simulations of real-world traffic flows while taking into account variables including vehicle movement, pedestrian interactions, and dynamics of public transportation. Planners can learn more about traffic bottlenecks, patterns of congestion, and potential remedies by evaluating these models.
Additionally, AIMSUN is not constrained to a static viewpoint. It makes it easier to simulate different situations, which enables planners to evaluate the possible effects of suggested changes to the transportation system. AIMSUN’s simulations offer a dynamic testing environment for comparing various solutions before implementation, whether it be for adding new transit lines, enforcing congestion pricing, or altering traffic signal timings.

15. HOMER
As it enters the limelight of micro-simulation and optimization, HOMER establishes itself as a dominant force. By focusing its powers on efficient traffic management and well-informed infrastructure planning, this software plays a crucial part in enabling detailed examination of urban transportation networks.
The importance of HOMER in the complex web of urban mobility resides in its capacity to pore over the details of transportation dynamics. The software equips urban specialists to build complex models that faithfully reproduce the complex interactions between autos, people, and transportation networks with a concentration on micro-simulation. Planners can better understand traffic patterns, bottlenecks, and prospective improvement locations by analyzing these models.

Conclusion:
As urban planning and design continue to evolve, these software tools offer a diverse range of capabilities that drive informed decision-making, holistic designs, and sustainable urban environments. Each tool serves as a testament to the power of technology in reshaping the urban landscape for a better future.

Urban Design Lab
About the Author
This is the admin account of Urban Design Lab. This account publishes articles written by team members, contributions from guest writers, and other occasional submissions. Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions or comments.
Related articles

Architecture Professional Degree Delisting: Explained
Periodic Table for Urban Design and Planning Elements


History of Urban Planning in India

Kim Dovey: Leading Theories on Informal Cities and Urban Assemblage
UDL GIS
Masterclass
GIS Made Easy – Learn to Map, Analyse, and Transform Urban Futures
Session Dates
23rd-27th February 2026

Urban Design Lab
Be the part of our Network
Stay updated on workshops, design tools, and calls for collaboration
Curating the best graduate thesis project globally!

Free E-Book
From thesis to Portfolio
A Guide to Convert Academic Work into a Professional Portfolio”
Recent Posts
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
Sign up for our Newsletter
“Let’s explore the new avenues of Urban environment together “