
Climate Change and Urban Design

Introduction
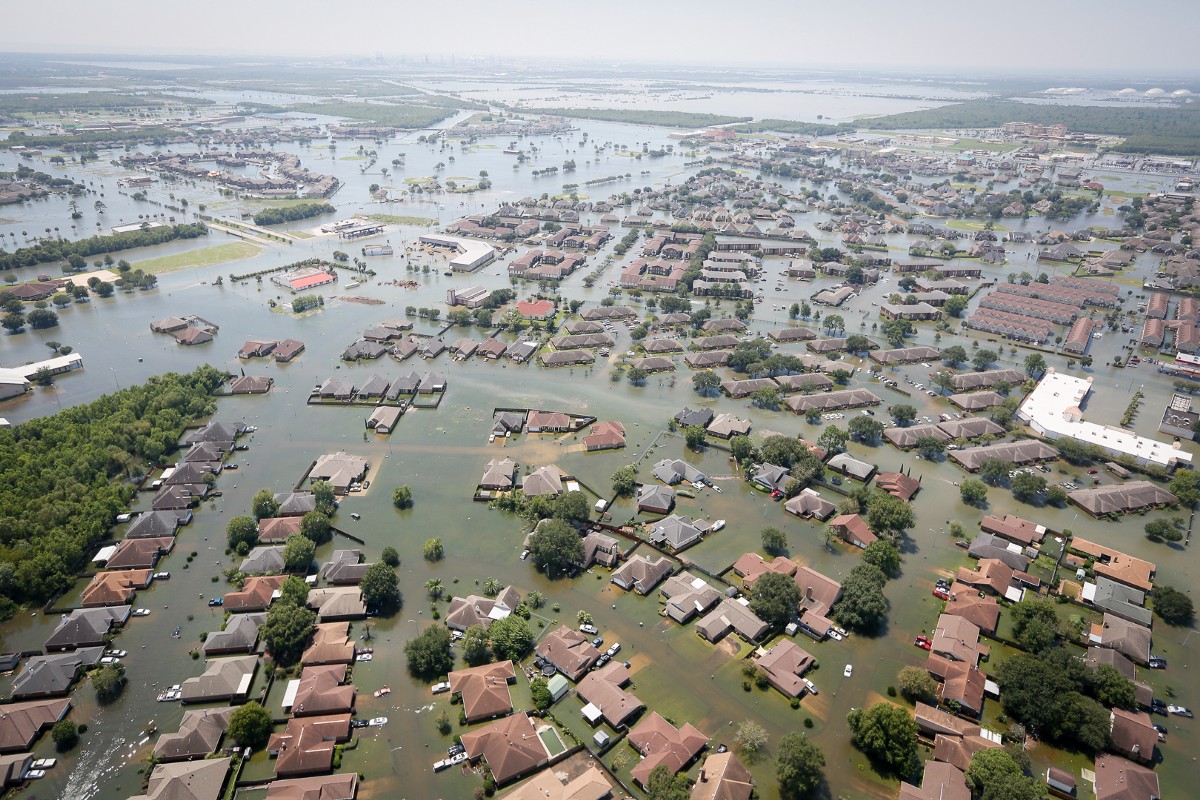
The rapidly escalating climate change phenomenon presents an immense and daunting challenge for urban centers worldwide, a recently published study has cautioned. The far-reaching consequences of this environmental crisis are poised to intensify remarkably over the forthcoming decades, exacerbating the precarious situation faced by densely populated metropolitan areas.
While concerted and collaborative efforts on a global scale may potentially mitigate the severity of these impacts, the overwhelming scientific evidence points to an inescapable reality: certain manifestations, such as intensified rainfall patterns, storm surges of unprecedented magnitude, and the urban heat island effect, are already unfolding and will persist unabated, irrespective of ongoing mitigation endeavors.
Remarkably, urban planning has emerged as a pivotal factor in developing and implementing adaptive responses tailored to the unique challenges faced by metropolitan environments. The universal nature of urban planning, coupled with its diverse array of tools, including comprehensive plan formulation, stakeholder engagement initiatives, development management protocols, and design standard enforcement, positions it as a potent force in fortifying urban resilience.
As cities brace themselves for the profound challenges posed by the climate crisis, the indispensable role of urban planning in crafting and operationalizing adaptive strategies has taken on a renewed sense of urgency and significance.

The Evolving Landscape of Urban Planning
The realm of urban planning for climate change mitigation and adaptation is undergoing a profound metamorphosis, shedding light on the multifaceted challenges and opportunities that arise in the pursuit of sustainable urban futures. This transformative transition necessitates an integrated and multidimensional approach that harmoniously combines mitigation strategies, adaptive measures, and a holistic vision for urban development.
As the spectre of climate change looms large, an imperative question arises: How can the disciplines of urban and regional planning empower communities to better prepare and adapt to the projected impacts of this environmental upheaval? This inquiry holds immense significance, as cities and towns worldwide grapple with the pressing need to fortify their resilience against the impending ramifications of a changing climate.

In this evolving landscape, urban planners find themselves at the vanguard of a concerted effort to equip municipalities with the necessary tools and strategies to navigate the intricate web of challenges posed by climate change. Their role transcends mere infrastructure planning, encompassing a comprehensive understanding of the intricate interplay between the built environment, natural ecosystems, and the socio-economic fabric of communities.
The multidisciplinary nature of urban planning positions it as a vital lynchpin in this endeavour, enabling the seamless integration of mitigation measures aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions, adaptive strategies to bolster resilience against climate-induced phenomena, and a holistic vision that prioritizes sustainable urban development. This synergistic approach holds the potential to catalyze transformative change, fostering the creation of urban environments that are not only resilient but also vibrant, equitable, and environmentally conscious.
As the world grapples with the inexorable march of climate change, the evolving landscape of urban planning emerges as a beacon of hope, illuminating pathways towards a future where cities and towns are fortified against the vagaries of a changing climate, while simultaneously nurturing the well-being and prosperity of their inhabitants.
The Role of Urban and Regional Planning
Urban and regional planning emerges as a potent and indispensable instrument for navigating the intricate terrain of land-use challenges, both in the immediate and distant horizons. Its unique duality, encompassing spatial and temporal dimensions, renders it an invaluable asset for the meticulous planning of large-scale infrastructure projects and the judicious management of urban growth trajectories. Notably, community engagement stands as a cornerstone of effective planning, fostering a spirit of co-design and forging vital partnerships that are essential for achieving sustainable solutions.

Implications of Planning for Climate Change
The formulation of urban planning strategies geared towards combating the existential threat of climate change necessitates a two-pronged approach, seamlessly integrating both mitigation and adaptation measures. However, for these endeavors to bear fruition, they must be firmly entrenched within overarching frameworks that transcend geographical boundaries, such as the United Nations’ ambitious Sustainable Development Goals and robust national urban policies. These comprehensive frameworks ensure that climate action initiatives permeate every echelon of governance and cut across myriad sectors, fostering a coordinated and holistic response.
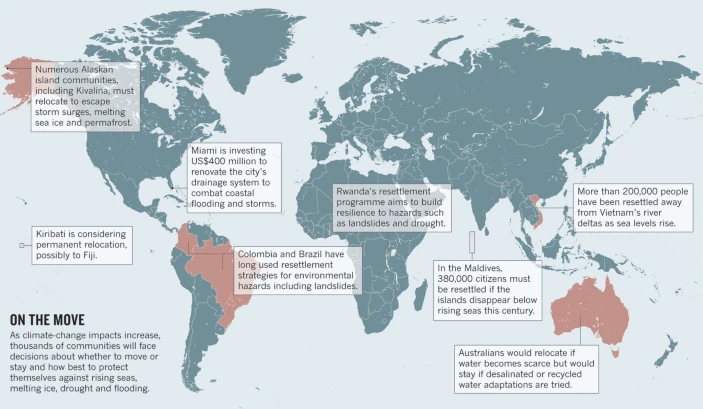
Addressing Climate-Induced Resettlement
Amidst the myriad of formidable obstacles posed by the relentless march of climate change, one of the most intricate and multifaceted quandaries lies in the inescapable need for the resettlement of entire communities rendered vulnerable by the escalating climate-induced risks. Extreme events of unprecedented magnitude, ranging from catastrophic floods to raging wildfires and the inexorable rise of sea levels, are rapidly rendering once-habitable areas unfit for human habitation, necessitating a proactive and strategic approach to resettle displaced populations.
This arduous undertaking demands a confluence of foresight, flexibility, and substantial investment of resources, as communities grapple with the profound implications of being uprooted from their ancestral homelands and the daunting task of establishing new settlements.
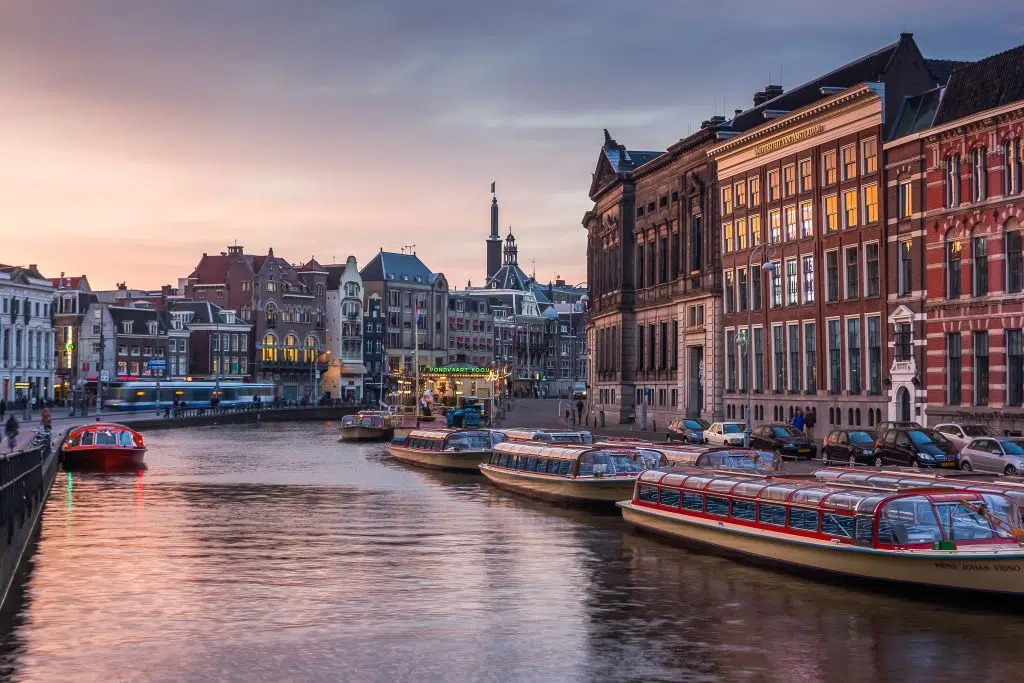
Case Study: Climate Resilience in Amsterdam
Sandwiched between Belgium and Germany in Western Europe, the tiny country of the Netherlands has been constantly battered by the North Sea. With one-third of its land situated below sea level, the country faces significant threats from climate change-triggered sea-level rise. Despite these challenges, the Netherlands strives to be ambitiously ahead in building climate resilience and adaptation. The visionary National Climate Adaptation Strategy (NAS), launched in 2016, spearheads numerous climate adaptation initiatives nationwide. This strategy transforms the climate threat into opportunities for a sustainable future and enhanced climate resilience. Amsterdam, the capital city, is second on the list of cities at risk of flooding by 2050, with projections suggesting that more than 700,000 people—97% of the city’s population—could be displaced by the end of the century. To combat this, the Netherlands implements efficient flood prevention and control systems, alongside innovative mitigation strategies, significantly boosting its climate resilience. The renowned Delta Programme, initiated in response to a devastating 1953 storm surge, has evolved to focus on climate adaptation, incorporating fresh water supply management, flood mitigation, and resilient spatial planning. These efforts make Amsterdam a model of how a country can turn climate challenges into resilient urban futures.

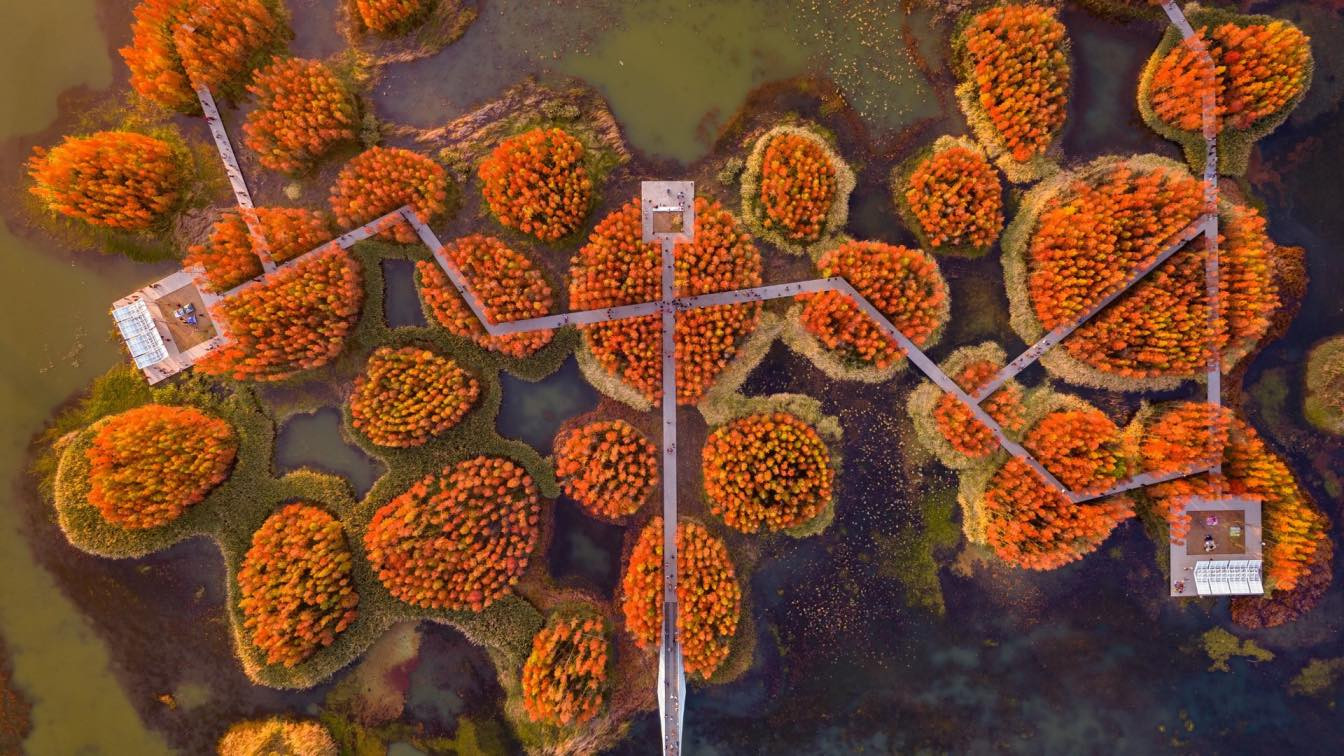
Case Study: Fish Tail Park, Nanchang, China
In Nanchang, China, Turenscape has created a transformative urban oasis, Fish Tail Park, within the Yangtze River floodplain. This innovative project, designed to mitigate the impacts of climate change, exemplifies the sponge city concept by managing stormwater, providing wildlife habitat, and offering recreational spaces. Drawing inspiration from ancient farming techniques, Turenscape converted a degraded 126-acre landscape into a floating forest with islets made from recycled materials. The park’s central lake can accommodate significant water-level fluctuations, crucial for flood management. Flood-adapted vegetation, including tree species and wetland plants, ensures resilience against monsoon floods. The park also features a network of boardwalks and recreational areas, merging urban life with nature and setting a precedent for sustainable urban development in regions with variable climates.

Case Study: Maldives Floating City , Maldives
From climate refugees to climate innovators – that is the vision of Dutch Docklands and the architects from Waterstudio for the people of the Maldives. The Maldives Floating City, the world’s first floating island city, aims to house around 20,000 people in a sustainable, resilient urban environment. Designed to combat rising sea levels threatening the archipelago, this city features colorful low-rise buildings, eco-friendly floating structures, and a layout inspired by brain corals. Positioned near Malé in a 200-hectare lagoon, the city integrates nature with urban living, utilizing smart power grids and artificial coral reefs to enhance marine biodiversity. With plans for homes, public buildings, and commercial spaces, this innovative project aspires to transform Maldivians from climate change victims into pioneers of climate adaptation.


Key Elements of Urban Planning for Climate Change

As the spectre of climate change looms large, the imperative for urban centers to fortify their defenses against its multifarious impacts has assumed paramount importance. Effective urban planning emerges as a potent bulwark against this formidable challenge, harnessing several crucial elements in a concerted effort to safeguard the well-being of metropolitan environments and their denizens.
1. Investing in Forward Strategic Planning: A Proactive Approach
At the vanguard of this endeavor lies the pressing need for investments in forward-thinking strategic planning initiatives. This proactive measure not only enables the implementation of mitigation strategies but also paves the way for comprehensive adaptation measures. Prudent infrastructure development and judicious growth management protocols form the bedrock of this long-term vision, ensuring that urban centers are equipped to withstand the vagaries of a rapidly evolving climatic landscape.
2. Embedding Climate Action in Planning Processes: An Integrative Approach
Recognizing the inextricable link between urban development and climate change, it is imperative to embed climate considerations as an integral component of all land use and development decisions. This holistic approach ensures that every facet of urban planning, from zoning regulations to infrastructure projects, is meticulously scrutinized through the lens of climate resilience, fostering a harmonious coexistence between human habitats and the natural environment.
3. Collaborative and Co-Design Practices: Harnessing Collective Wisdom
The intricate tapestry of urban ecosystems necessitates a participatory and inclusive approach, with urban planners actively engaging diverse communities and leveraging interdisciplinary expertise. Through collaborative practices and co-design methodologies, the collective wisdom of stakeholders is harnessed, resulting in resilient urban environments that prioritize sustainability, adaptability, and the well-being of all inhabitants.
4. Continuous Evaluation and Monitoring: Ensuring Sustained Commitment
To ensure that the promises of climate-resilient urban planning are upheld and maintained over time, a robust framework for continuous evaluation and monitoring is indispensable. This rigorous approach not only validates the efficacy of implemented strategies but also facilitates course corrections and refinements as needed, ensuring that promised outcomes, such as the realization of carbon-neutral developments, are consistently achieved and sustained.
As urban centers grapple with the existential threat posed by climate change, the pivotal role of urban planning in crafting adaptive and resilient solutions has assumed unprecedented significance, underscoring the urgent need for a concerted and multifaceted approach to safeguarding the future of our metropolitan environments.

Future Challenges and Opportunities
As the world grapples with the escalating climate crisis, the realm of urban planning finds itself at the forefront of a monumental challenge – one that demands innovative solutions and an unwavering commitment to safeguarding the future of our cities. Peering into the horizon, a multitude of critical imperatives must be addressed to ensure that urban planning emerges as a formidable force in the fight against climate change.
Community and Cultural Tapestry: Tailoring approaches to the intricate tapestry of local contexts, particularly in developing nations where resources may be scarce, emerges as a paramount priority. Only by embracing the nuances of diverse communities can truly effective and inclusive strategies be forged.
Unwavering Leadership: Ensuring strong and resolute leadership at all echelons of governance and across sectors is imperative to catalyze and sustain climate action. A united front, driven by visionary stewardship, is the clarion call of our times.
Fostering Innovation: Encouraging and nurturing local innovations, while seamlessly adopting cutting-edge technologies, holds the key to enhancing urban resilience. Embracing the spirit of ingenuity and adaptability is essential to navigate the uncharted waters of climate change.
Regulatory Resolve: Implementing robust regulatory frameworks that demand compliance and ensure long-term sustainability is a non-negotiable necessity. Enforcement and accountability must be the cornerstones upon which a climate-resilient future is built.
Farsighted Planning: Developing comprehensive plans that extend their gaze far beyond the immediate horizon, accounting for the profound and far-reaching impacts of climate change, is of paramount importance – particularly when it comes to major infrastructure projects that will shape the urban landscapes of tomorrow.
As cities around the world brace themselves for the formidable challenges posed by the climate crisis, the pivotal role of urban planning in charting a course towards a sustainable and resilient future has never been more crucial. It is a clarion call that demands unwavering dedication, innovative thinking, and a steadfast commitment to preserving the essence of our urban oases for generations to come.
UDL Photoshop Masterclass
Decipher the secrets of Mapping and 3D Visualisation

Urban Design Lab
About the Author
This is the admin account of Urban Design Lab. This account publishes articles written by team members, contributions from guest writers, and other occasional submissions. Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions or comments.
Related articles

Architecture Professional Degree Delisting: Explained
Periodic Table for Urban Design and Planning Elements


History of Urban Planning in India

UDL Illustrator
Masterclass
Visualising Urban and Architecture Diagrams
Session Dates
28th-29th March 2026

Urban Design Lab
Be the part of our Network
Stay updated on workshops, design tools, and calls for collaboration
Curating the best graduate thesis project globally!

Free E-Book
From thesis to Portfolio
A Guide to Convert Academic Work into a Professional Portfolio”
Recent Posts
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
Sign up for our Newsletter
“Let’s explore the new avenues of Urban environment together “






































One Comment