GIS as a tool for Urban Planning

Although the world’s population is expanding quickly, there is only a limited amount of land that can sustain it. In fact, its size is getting smaller by the day. The new threat facing the environment is urbanization. Despite deliberately encroaching on natural areas, humans still struggle to provide adequate living circumstances for everyone. Smart urbanization, or planning urban growth in a way that allows for more people to be accommodated in a smaller space, is now more important than ever. GIS is now widely used. Today, it is present in practically every aspect of human life. How is it possible in such a situation for the magic of GIS to escape the realm of daily life? Planners can expand the boundaries of urbanization by using GIS in urban planning.
Using GIS to plan cities
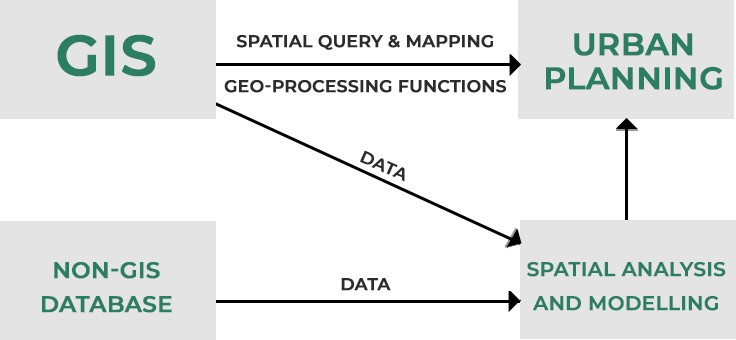
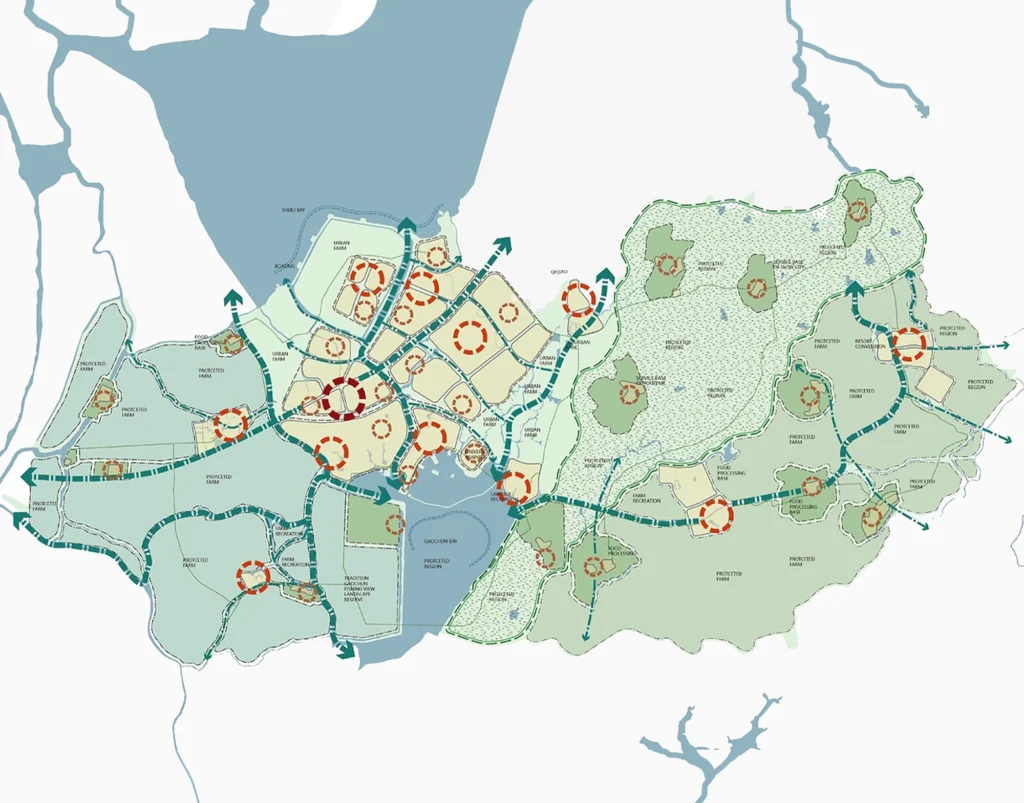
GIS provides planners, surveyors, and engineers with the tools they need to design and map their neighborhoods and cities. Visualization, spatial analysis, and spatial modeling are the most frequently used GIS functions in plan making. GIS can help to store, manipulate, and analyze the physical, social, and economic data of a city. Planners can then use the spatial query and mapping functions of GIS to analyze the existing situation in the city. Through map overlay analysis, GIS can help to identify areas of conflict of land development with the environment by overlaying existing land development on land suitability maps.
Using the multilayered mapping feature of GIS, a municipal planning committee can visualize a variety of things, for instance, prime agricultural land, surface water, high flood frequency, and highly erodible land. This information leads to informed decisions such as avoiding developing areas with high flood frequency as those areas are not likely to attract dwellers. When doing a feasibility assessment of a location for a particular purpose, such as determining if a site is suitable for the construction of a bridge or dam, GIS can be a great help. GIS can be used to carry out feasibility studies for smaller structures like schools and hospitals. It can also be used to determine if a location is suitable for garbage treatment and disposal. Additionally, GIS aids in recognizing shifts in a land’s behavior or geographical characteristics over a given period of time. Professionals may plan effectively and make informed decisions on the state of an area’s growth with the use of this information. Planners make use of GIS to smooth the progress of public participation and community input as they develop a vision for the community that enhances the quality of life for all citizens.
Usefulness of GIS for Urban Planners
There are numerous benefits of using GIS in urban planning, but here are the few important ones.
1. Improved mapping
Since all of a region’s maps and data can be kept in one central location, GIS can boost map credibility (how current a map is), boost the effectiveness of thematic mapping, and reduce data storage costs.
2. Increased access to vital information
Desktop GIS simplifies the process of collecting, organising, and retrieving information from a wide range of sources. Similar to traditional GIS, cloud-based GIS provides this perk while also making it possible to view data from any mobile device.
3. Improved communication
Employees don’t have to waste time hunting down information across departments or sifting through piles of paperwork when they can just log in to a central database that stores and organises all of the company’s data.
4. Increased quality and efficiency for public services
In order to facilitate communication between government agencies and the general public, GIS can be utilised to build a portal that is accessible to the general populace. Information may be promptly disseminated between government personnel, and the public can get the data it requires on its own.
5. Increased support for strategic decision making
Planners can more quickly access a wider variety of crucial geographic information and more efficiently develop well-informed strategies. Additionally, they can consider a wider variety of “what-if” scenarios, which should help them develop longer-term plans that are stronger and more successful.
The application of GIS in urban planning
Here are some of the practical applications of GIS in urban planning.
1. Resource Inventory

The collection of land use and environmental information is essential in urban planning. This is usually a time-consuming exercise because human beings do it manually and even when done in computers, one gets tired quickly because he or she is required to input the data manually. Using geographical information, together with remote sensing helps in the timely collection of both the environmental and land use information. In urban areas, remote sensing images are becoming an essential source of getting three-dimensional information for urban areas. The use of land and any changes that may occur in urban areas are detected using the above techniques.
2. Creating land-use maps & plans

Future land-use maps act as a community’s guide to future infrastructure, build plans, and public spaces. These maps help ensure that a city’s urban planning accounts for environmental conservation, pollution, mitigating transportation issues, and limiting urban sprawl.
With GIS, urban planners can quickly create maps of the city as it is today, and then use various modeling and predictive data techniques to explore scenarios for the future. Ideally using this exercise to create a future land-use map that is thoughtful, sustainable, and sound.
3. Planning applications

GIS can help the government and businesses process and organize planning applications.
Many GIS portals can be made public facing, which means citizens can access data such as parcel outlines and information, county/district boundaries, and area zoning. With vital information more widely available to all, government resources (which might have been spent fielding these requests and finding the data) can be put to use elsewhere.
Moreover, with all the applications stored in a central database, organization, processing, and status tracking becomes much simpler.
4. Analyzing socioeconomic & environmental data

Creating future land-use maps must take into account several environmental scenarios, as well as project future demand for land resources. Modeling must include population data, economic activities, and spatial distribution.
5. Land suitability analysis/site selection

Urban planners can perform land suitability analysis, a crucial stage in site selection, using GIS tools like map overlay. Urban planners can identify environmentally sensitive areas with the aid of remote sensing, spatial queries, and environmental data analysis. They can spot any areas where potential development would conflict with the environment by superimposing existing land development on maps of land suitability.
6. Measuring connectivity

GIS geoprocessing functions like map overlay, buffering, and spatial analysis help urban planners to conduct connectivity measurement.
Connectivity refers to how easy it is to walk or bike in a given city. A highly-connected area will give its residents numerous options to get from A to B quickly.
7. Impact assessments

An environmental impact assessment can be conducted to evaluate the potential effects urban development will have on the environment. If issues are found, the urban planner can then recommend ways to alleviate or mitigate negative outcomes.
8. Evaluation, monitoring, & feedback

GIS tools can help evaluate a building plan, monitor the project after completion, and even gather feedback to help make improvements.
Together with remote sensing, GIS can help planners to track if development is following the area’s land use plan. It can also help them evaluate impact and suggest adjustments – if required.
GIS enables urban planners to create the towns and cities where we live, plan for the future, and make adjustments as the local population shifts. GIS is a significant and practical tool that has grown to be extremely valuable for many when it comes to efficient urban planning.

Urban Design Lab
About the Author
This is the admin account of Urban Design Lab. This account publishes articles written by team members, contributions from guest writers, and other occasional submissions. Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions or comments.
Related articles

Architecture Professional Degree Delisting: Explained
Periodic Table for Urban Design and Planning Elements


History of Urban Planning in India

Kim Dovey: Leading Theories on Informal Cities and Urban Assemblage
UDL GIS
Masterclass
GIS Made Easy – Learn to Map, Analyse, and Transform Urban Futures
Session Dates
23rd-27th February 2026

Urban Design Lab
Be the part of our Network
Stay updated on workshops, design tools, and calls for collaboration
Curating the best graduate thesis project globally!

Free E-Book
From thesis to Portfolio
A Guide to Convert Academic Work into a Professional Portfolio”
Recent Posts
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
- Article Posted:
Sign up for our Newsletter
“Let’s explore the new avenues of Urban environment together “