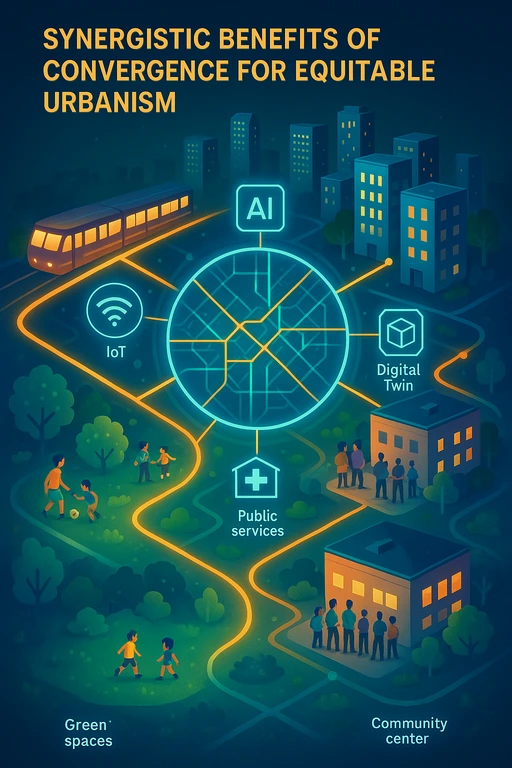
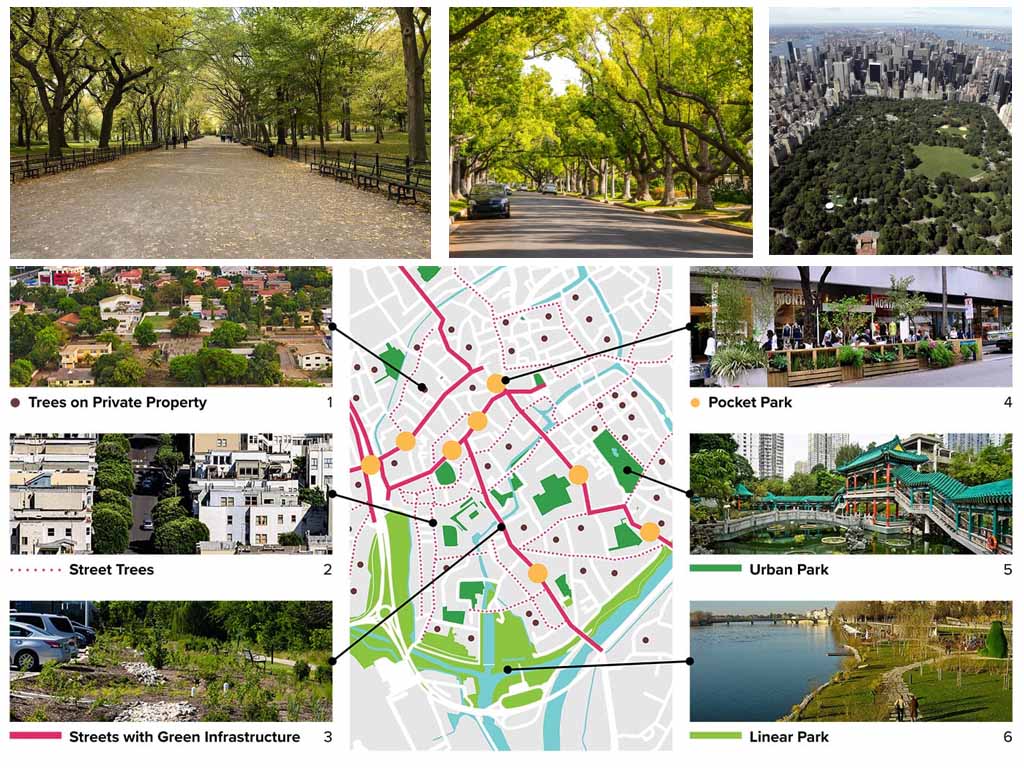
This post explores how combining Geographic Information Systems (GIS) with emerging technologies can foster equitable urbanism. As urbanization accelerates, it intensifies existing inequalities, making the fair distribution of resources and opportunities a critical global goal. GIS helps identify disparities in services, resources, and environmental burdens, while technologies like AI, Machine Learning (ML), IoT, Digital Twins, and Remote Sensing enhance GIS capabilities. AI and ML offer predictive insights, IoT enables real-time monitoring of urban services, Digital Twins support scenario planning and public engagement, and Remote Sensing maps inequality and environmental justice issues.
These technologies, when integrated with GIS, provide a powerful platform for data-driven decision-making, optimizing urban services, and addressing social equity. However, challenges arise, including algorithmic bias, privacy concerns, and the digital divide. Algorithmic bias can reinforce existing inequalities, while extensive data collection raises privacy and security issues. The digital divide may exclude marginalized populations from accessing the benefits of smart city initiatives, and governance inefficiencies could hinder equitable implementation. To ensure these technologies genuinely serve all urban residents, it is vital to address these ethical and practical challenges. If left unaddressed, these risks could prevent the full realization of equitable urban development.




















































One Comment
I really appreciate content like this—it’s clear, informative, and actually helpful. Definitely worth reading!